Probenecid: novel use as a non-injurious positive inotrope acting via cardiac TRPV2 stimulation
- PMID: 22561103
- PMCID: PMC3372642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.04.011
Probenecid: novel use as a non-injurious positive inotrope acting via cardiac TRPV2 stimulation
Abstract
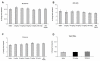
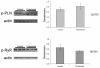
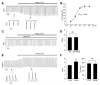
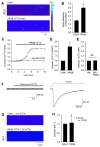
Probenecid is a highly lipid soluble benzoic acid derivative originally used to increase serum antibiotic concentrations. It was later discovered to have uricosuric effects and was FDA approved for gout therapy. It has recently been found to be a potent agonist of transient receptor potential vanilloid 2 (TRPV2). We have shown that this receptor is in the cardiomyocyte and report a positive inotropic effect of the drug. Using echocardiography, Langendorff and isolated myocytes, we measured the change in contractility and, using TRPV2(-/-) mice, proved that the effect was mediated by TRPV2 channels in the cardiomyocytes. Analysis of the expression of Ca(2+) handling and β-adrenergic signaling pathway proteins showed that the contractility was not increased through activation of the β-ADR. We propose that the response to probenecid is due to activation of TRPV2 channels secondary to SR release of Ca(2+).
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Beyer RH, Wiebelhaus VD, Russe HF, Peck HM, McKinney SE. Benemid: An anticatabolite; its pharmacological properties. Fed Proc. 1950;9:258.
-
- Beyer KH, Russo HF, Tillson EK, Miller AK, Verwey WF, Gass SR. Benemid,’ p-(di-n-propylsulfamyl)-benzoic acid; its renal affinity and its elimination. Am J Physiol. 1951;166(3):625–40. - PubMed
-
- Boger WP, Beatty JO, Pitts F, Flippin HF. The influence of a new benzoic acid derivative on the metabolism of para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS) and penicillin. Ann Intern Med. 1950A;33(1):18–31. - PubMed
-
- Boger WP, Pitts FW, Gallagher ME. Benemid and Carinamide: Comparison of effect on Para-amino-salicylic acid (PAS) Plasma Concentrations. J of Lab Clin Med. 1950B;36:276–82. - PubMed
-
- Boger WP, Strickland SC. Probenecid (Benemid): Its uses and side effects in 2502 Patients. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1955;95:83–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 ES017263/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL091478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL007382/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL026057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ES017263/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL64018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T1 UL1RR026314/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007382/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR026314/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL26057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL026057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

