Germs gone wild
- PMID: 22561817
- PMCID: PMC3698559
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2767
Germs gone wild
Abstract
The normally harmless behavior of bacteria in the intestinal tract is maintained by community structure and the integrity of host defenses. When either or both of these are compromised, a few disgruntled outcasts can cause a riot, taking down the whole neighborhood (pages 799-806).
Figures
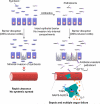
Comment on
-
Lethal inflammasome activation by a multidrug-resistant pathobiont upon antibiotic disruption of the microbiota.Nat Med. 2012 May;18(5):799-806. doi: 10.1038/nm.2729. Nat Med. 2012. PMID: 22522562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Macpherson AJ, Harris NL. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:478–485. - PubMed
-
- Beaugerie L, Petit JC. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;18:337–352. - PubMed
-
- Backhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI. Science. 2005;307:1915–1920. - PubMed
-
- Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S, Medzhitov R. Cell. 2004;118:229–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

