Effect of chronic intracerebroventricluar administration of lipopolysaccharide on connexin43 protein expression in rat hippocampus
- PMID: 22562029
- PMCID: PMC3614252
- DOI: 10.6091/ibj.1030.2012
Effect of chronic intracerebroventricluar administration of lipopolysaccharide on connexin43 protein expression in rat hippocampus
Abstract
Background: Hippocampal damages, which are accompanied by inflammation, are among the main causes of epilepsy acquisition. We previously reported that chronic intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) modulates epileptogenesis in rats. There is a network of gap junction channels in the hippocampus that contribute to epileptogenesis. Gap junction channels are formed by oligomeric protein subunits called connexins (Cx). Astrocytic Cx43 and neuronal Cx36 are expressed in the hippocampus. In order to find out the possible role of gap junctions in seizure-modulating effect of LPS and neuroinflammation, we studied the effect of central administration of LPS on expression of Cx36 and Cx43 in rat hippocampus.
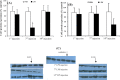
Methods: LPS, 2.5 mug/rat/day, was injected i.c.v. to male Wistar rats for 14 days. mRNA and protein abundance of Cx36, Cx43 and IL1-β were measured in rat hippocampus by real time-PCR, Western blot and ELISA techniques, at the beginning, in the middle, and at the end of the treatment period.
Results: IL1-β protein level was significantly increased 6 h after first injection of LPS. Cx36 and Cx43 mRNA expression did not alter during chronic administration of LPS. A selective decrease in Cx43 protein expression was observed after 7 injections of LPS.
Conclusion: It is suggested that Cx43 containing gap junctions in the hippocampus is down-regulated in response to chronic injection of LPS. This event can inhibit propagation of toxic and noxious molecules to neighboring cells and modulate hippocampal excitability and epileptogenesis.
Figures


References
-
- Ambrosini A, Louin G, Croci N, Plotkine M, Jafarian-Tehrani M. Characterization of a rat model to study acute neuroinflammation on histopathological, bio-chemical and functional outcomes. J Neurosci Methods. 2005 Jun;144(2):183–91. - PubMed
-
- Meme W, Calvo CF, Froger N, Ezan P, Amigou E, Koulakoff Aetal. Proinflammatory cytokines released from microglia inhibit gap junctions in astrocytes: potentiation by beta-amyloid. FASEB J. 2006 Mar;20(3):494–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
