Early and late motor responses to action observation
- PMID: 22563004
- PMCID: PMC3739914
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nss049
Early and late motor responses to action observation
Abstract
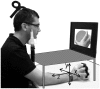
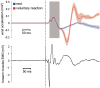
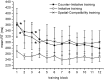
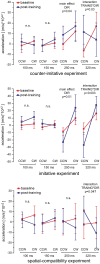
Is a short visuomotor associative training sufficient to reverse the visuomotor tuning of mirror neurons in adult humans? We tested the effects of associative training on corticospinal modulation during action observation in the 100-320 ms interval after action onset. In two separate experiments, the acceleration of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)-induced movements was recorded before and after training participants to respond to observed acts with an opposite or similar behavior. Before training, TMS-induced accelerations mirrored the observed action at 250 and 320 ms. After training, responses at 250 ms were unchanged and still mirrored the stimuli, without any effect of training direction. Only at 320 ms, we observed training-dependent changes in evoked responses. A control experiment with non-biological rotational movements as visual stimuli indicated that spatial stimulus-response compatibility is not sufficient to account for the results of the two main experiments. We show that the effects of a short visuomotor associative training are not pervasive on the automatic mirror responses. 'Early' (250 ms) responses were not influenced by training. Conversely only 'late' (320 ms) responses changed according to the training direction. This biphasic time course indicates that two distinct mechanisms produce the automatic mirror responses and the newly learned visuomotor associations.
Keywords: action observation; action selection; associative sequence learning; mirror neurons; transcranial magnetic stimulation; visual motor training.
Figures

References
-
- Amassian VE, Cracco RQ, Maccabee PJ, Cracco JB, Rudell A, Eberle L. Suppression of visual perception by magnetic coil stimulation of human occipital cortex. Electroencephalography & Clinical Neurophysiology. 1989;74:458–62. - PubMed
-
- Aron AR, Robbins TW, Poldrack RA. Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 2004;8:170–7. - PubMed
-
- Avenanti A, Bolognini N, Maravita A, Aglioti SM. Somatic and motor components of action simulation. Current Biology. 2007;17:2129–35. - PubMed
-
- Barrett KE, Barman SM, Boitano S, Brooks HL. Ganong's Review of Medical Physiology. 23rd edn. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2009.
-
- Bernier PM, Burle B, Hasbroucq T, Blouin J. Spatio-temporal dynamics of reach-related neural activity for visual and somatosensory targets. Neuroimage. 2009;47:1767–77. - PubMed

