Pathological alteration in the choroid plexus of Alzheimer's disease: implication for new therapy approaches
- PMID: 22563316
- PMCID: PMC3342675
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00075
Pathological alteration in the choroid plexus of Alzheimer's disease: implication for new therapy approaches
Abstract
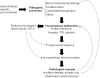
Morphological alterations of choroid plexus in Alzheimer's disease (AD) have been extensively investigated. These changes include epithelial atrophy, thickening of the basement membrane, and stroma fibrosis. As a result, synthesis, secretory, and transportation functions are significantly altered resulting in decreased cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) turnover. Recent studies discuss the potential impacts of these changes, including the possibility of reduced resistance to stress insults and slow clearance of toxic compounds from CSF with specific reference to the amyloid peptide. Here, we review new evidences for AD-related changes in the choroid plexus. The data suggest that the significantly altered functions of the choroid plexus contribute to the multiparametric pathogenesis of late-onset AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid; cell death; choroid plexus; mitochondria; oxidative stress.
Figures

References
-
- Aliyev A., Seyidova D., Rzayev N., Obrenovich M. E., Lamb B. T., Chen S. G., Smith M. A., Perry G., De La Torre J. C., Aliev G. (2004). Is nitric oxide a key target in the pathogenesis of brain lesions during the development of Alzheimer’s disease? Neurol. Res. 26, 547–55310.1179/01610425017613 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anthony S. G., Schipper H. M., Tavares R., Hovanesian V., Cortez S. C., Stopa E. G., Johanson C. E. (2003). Stress protein expression in the Alzheimer-diseased choroid plexus. J. Alzheimers Dis. 5, 171–177 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

