Effect of an L- and T-type calcium channel blocker on 24-hour systolic blood pressure and heart rate in hypertensive patients
- PMID: 22563335
- PMCID: PMC3341419
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.4.231
Effect of an L- and T-type calcium channel blocker on 24-hour systolic blood pressure and heart rate in hypertensive patients
Abstract
Background and objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of an L- and T-type calcium channel blocker (CCB) on 24-hour systolic blood pressure (24-hour SBP) and heart rate (24-hour HR) profiles in essential hypertensive patients.
Subjects and methods: Thirty-seven consecutive patients were enrolled in this study. The 24-hour SBP and HR were recorded before and after treatment with efonidipine (L- and T-type CCB, 40 mg), after waking. Changes in 24-hour SBP and HR and the diurnal to nocturnal SBP ratio were measured. The best-fit curves of changes in SBP and HR were depicted using a periodic function.
Results: The mean 24-hour SBP and HR decreased significantly after treatment. The diurnal to nocturnal SBP ratio in dipper-type hypertension cases decreased from 16.7±6.1% to 8.3±9.8% (p<0.05), whereas in non-dipper hypertension cases, it increased from 2.3±2.9% to 7.7±5.1% (p<0.01). The antihypertensive effect was minimal at 5.0 hours after drug administration and it slowly recovered at a constant rate (2.1 mm Hg/h) over 12 hours in dipper cases. The median 24-hour changes in HR in the dipper and non-dipper cases were -2.3/min and -5.4/min, respectively. A continuous reduction in the change in HR was seen from 3.5 to 23 hours after drug administration.
Conclusion: The antihypertensive action of efonidipine was characterized by a slow recovery of the SBP decrease at a constant rate (2.1 mm Hg/h) and a non-administration time dependent reduction in 24-hour HR.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Calcium channel blockers; Heart rate; Hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

 : average systolic blood pressure before drug administration,
: average systolic blood pressure before drug administration,  : average systolic blood pressure after drug administration,
: average systolic blood pressure after drug administration,  : average heart rate before drug administration,
: average heart rate before drug administration,  : average heart rate after drug administration. Each value represents an average value±SD. *p<0.05, †p<0.01.
: average heart rate after drug administration. Each value represents an average value±SD. *p<0.05, †p<0.01.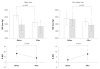

References
-
- Mancia G, de Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2007 guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) J Hypertens. 2007;25:1105–1187. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi K, Wakino S, Sugano N, Ozawa Y, Homma K, Saruta T. Ca2+ channel subtypes and pharmacology in the kidney. Circ Res. 2007;100:342–353. - PubMed
-
- Masumiya H, Shijuku T, Tanaka H, Shigenobu K. Inhibition of myocardial L- and T-type Ca2+ currents by efonidipine: possible mechanism for its chronotropic effect. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;349:351–357. - PubMed
-
- Ge W, Ren J. Combined L-/T-type calcium channel blockers: ready for prime time. Hypertension. 2009;53:592–594. - PubMed
-
- Perez-Reyes E. Molecular physiology of low-voltage-activated t-type calcium channels. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:117–161. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

