Phytoalexins of the Pyrinae: Biphenyls and dibenzofurans
- PMID: 22563359
- PMCID: PMC3343287
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.8.68
Phytoalexins of the Pyrinae: Biphenyls and dibenzofurans
Abstract
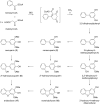
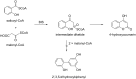
Biphenyls and dibenzofurans are the phytoalexins of the Pyrinae, a subtribe of the plant family Rosaceae. The Pyrinae correspond to the long-recognized Maloideae. Economically valuable species of the Pyrinae are apples and pears. Biphenyls and dibenzofurans are formed de novo in response to infection by bacterial and fungal pathogens. The inducible defense compounds were also produced in cell suspension cultures after treatment with biotic and abiotic elicitors. The antimicrobial activity of the phytoalexins was demonstrated. To date, 10 biphenyls and 17 dibenzofurans were isolated from 14 of the 30 Pyrinae genera. The most widely distributed compounds are the biphenyl aucuparin and the dibenzofuran γ-cotonefuran. The biosynthesis of the two classes of defense compounds is not well understood, despite the importance of the fruit crops. More recent studies have revealed simultaneous accumulation of biphenyls and dibenzofurans, suggesting sequential, rather than the previously proposed parallel, biosynthetic pathways. Elicitor-treated cell cultures of Sorbus aucuparia served as a model system for studying phytoalexin metabolism. The key enzyme that forms the carbon skeleton is biphenyl synthase. The starter substrate for this type-III polyketide synthase is benzoyl-CoA. In apples, biphenyl synthase is encoded by a gene family, members of which are differentially regulated. Metabolism of the phytoalexins may provide new tools for designing disease control strategies for fruit trees of the Pyrinae subtribe.
Keywords: Pyrinae; Sorbus aucuparia; biphenyls; dibenzofurans; phytoalexins.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential effect of elicitors on biphenyl and dibenzofuran formation in Sorbus aucuparia cell cultures.J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Nov 24;58(22):11977-84. doi: 10.1021/jf1026857. Epub 2010 Oct 20. J Agric Food Chem. 2010. PMID: 20961041
-
Biphenyls and dibenzofurans of the rosaceous subtribe Malinae and their role as phytoalexins.Planta. 2023 Sep 9;258(4):78. doi: 10.1007/s00425-023-04228-7. Planta. 2023. PMID: 37689618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis of the biphenyl phytoalexin aucuparin in Sorbus aucuparia cell cultures treated with Venturia inaequalis.Phytochemistry. 2013 Dec;96:101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Phytochemistry. 2013. PMID: 24074553
-
Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a biphenyl phytoalexin-specific O-methyltransferase from apple cell suspension cultures.Planta. 2019 Mar;249(3):677-691. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-3031-6. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Planta. 2019. PMID: 30357505
-
Biosynthesis of biphenyls and benzophenones--evolution of benzoic acid-specific type III polyketide synthases in plants.Phytochemistry. 2009 Oct-Nov;70(15-16):1719-27. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.06.017. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Phytochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19699497 Review.
Cited by
-
Biphenyl 4-Hydroxylases Involved in Aucuparin Biosynthesis in Rowan and Apple Are Cytochrome P450 736A Proteins.Plant Physiol. 2015 Jun;168(2):428-42. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00074. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25862456 Free PMC article.
-
Biphenyl Phytoalexin in Sorbus pohuashanensis Suspension Cell Induced by Yeast Extract.Molecules. 2016 Sep 14;21(9):1180. doi: 10.3390/molecules21091180. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27649118 Free PMC article.
-
Rowanberry-A Source of Bioactive Compounds and Their Biopharmaceutical Properties.Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 11;12(18):3225. doi: 10.3390/plants12183225. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nature-Inspired Biphenyls and Diphenyl Ethers: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation.ACS Omega. 2025 May 16;10(21):22028-22035. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c02099. eCollection 2025 Jun 3. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40488058 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of early genetic biomarkers for apple replant disease.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 24;15(9):e0238876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238876. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32970702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Potter D, Eriksson T, Evans R C, Oh S, Smedmark J E E, Morgan D R, Kerr M, Robertson K R, Arsenault M, Dickinson T A, et al. Plant Syst Evol. 2007;266:5–43. doi: 10.1007/s00606-007-0539-9. - DOI
-
- Paxton J D. J Phytopathol. 1981;101:106–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0434.1981.tb03327.x. - DOI
-
- Kokubun T, Harborne J B. Phytochemistry. 1995;40:1649–1654. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(95)00443-B. - DOI
-
- Kokubun T, Harborne J B, Eagles J, Waterman P G. Phytochemistry. 1995;38:57–60. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(94)00636-8. - DOI
-
- Burden R S, Kemp M S, Wiltshire C W, Owen J D. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 1. 1984:1445–1448. doi: 10.1039/P19840001445. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
