Lipopolysaccharide induces lung fibroblast proliferation through Toll-like receptor 4 signaling and the phosphoinositide3-kinase-Akt pathway
- PMID: 22563417
- PMCID: PMC3338545
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035926
Lipopolysaccharide induces lung fibroblast proliferation through Toll-like receptor 4 signaling and the phosphoinositide3-kinase-Akt pathway
Abstract
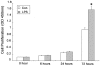
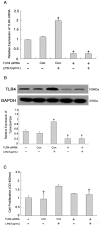
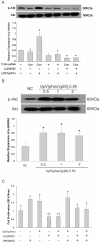
Pulmonary fibrosis is characterized by lung fibroblast proliferation and collagen secretion. In lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI), aberrant proliferation of lung fibroblasts is initiated in early disease stages, but the underlying mechanism remains unknown. In this study, we knocked down Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression in cultured mouse lung fibroblasts using TLR4-siRNA-lentivirus in order to investigate the effects of LPS challenge on lung fibroblast proliferation, phosphoinositide3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt pathway activation, and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) expression. Lung fibroblast proliferation, detected by BrdU assay, was unaffected by 1 mug/mL LPS challenge up to 24 hours, but at 72 hours, cell proliferation increased significantly. This proliferation was inhibited by siRNA-mediated TLR4 knockdown or treatment with the PI3K inhibitor, Ly294002. In addition, siRNA-mediated knockdown of TLR4 inhibited the LPS-induced up-regulation of TLR4, down-regulation of PTEN, and activation of the PI3K-Akt pathway (overexpression of phospho-Akt) at 72 hours, as detected by real-time PCR and Western blot analysis. Treatment with the PTEN inhibitor, bpV(phen), led to activation of the PI3K-Akt pathway. Neither the baseline expression nor LPS-induced down-regulation of PTEN in lung fibroblasts was influenced by PI3K activation state. PTEN inhibition was sufficient to exert the LPS effect on lung fibroblast proliferation, and PI3K-Akt pathway inhibition could reverse this process. Collectively, these results indicate that LPS can promote lung fibroblast proliferation via a TLR4 signaling mechanism that involves PTEN expression down-regulation and PI3K-Akt pathway activation. Moreover, PI3K-Akt pathway activation is a downstream effect of PTEN inhibition and plays a critical role in lung fibroblast proliferation. This mechanism could contribute to, and possibly accelerate, pulmonary fibrosis in the early stages of ALI/ARDS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor 4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced collagen secretion by phosphoinositide3-kinase-Akt pathway in fibroblasts during acute lung injury.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2009;29(2):119-25. doi: 10.1080/10799890902845690. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2009. PMID: 19519177
-
Lipopolysaccharide promotes lung fibroblast proliferation through autophagy inhibition via activation of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway.Lab Invest. 2019 May;99(5):625-633. doi: 10.1038/s41374-018-0160-2. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Lab Invest. 2019. PMID: 30760865
-
The role of TLR4-mediated PTEN/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway in neuroinflammation in hippocampal neurons.Neuroscience. 2014 Jun 6;269:93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.03.039. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24680857
-
Research Progress of PI3K/PTEN/AKT Signaling Pathway Associated with Renal Cell Carcinoma.Dis Markers. 2022 Aug 21;2022:1195875. doi: 10.1155/2022/1195875. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. Retraction in: Dis Markers. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9756735. doi: 10.1155/2023/9756735. PMID: 36046376 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
PI3K/PTEN signaling in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis.Adv Cancer Res. 2009;102:19-65. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(09)02002-8. Adv Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19595306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of CD14 and TLR4 in type I, type III collagen expression, synthesis and secretion in LPS-induced normal human skin fibroblasts.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Feb 15;8(2):2429-34. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25932184 Free PMC article.
-
Annexin A1 Mimetic Peptide AC2-26 Inhibits Sepsis-induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis through LXA4/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Curr Med Sci. 2018 Dec;38(6):997-1004. doi: 10.1007/s11596-018-1975-1. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Curr Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30536061
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced fibroblast proliferation by inducing toll-like receptor 4.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016 Jan 26;17:43. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-0895-0. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016. PMID: 26813112 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Variation and Gene Expression Levels of Tight Junction Genes Indicates Relationships Between PTEN as well as MAGI1 and Microscopic Colitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Jan;63(1):105-112. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4857-7. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29204743 Free PMC article.
-
Vimentin regulation of autophagy activation in lung fibroblasts in response to lipopolysaccharide exposure in vitro.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Feb;9(4):304. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5129. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33708931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howell DCJ, Falzon M, Bilbe N, Bottoms SE, Laurent GJ, et al. Pulmonary fibrosis is an early feature of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Thorax. 2006;61:Ii51–Ii51.
-
- Tasaka S, Ishizaka A. [Pulmonary fibrosis caused by ARDS]. Nippon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2005;94:1106–1111. - PubMed
-
- Tian J, Wang Y, He Z, Gao Y, Rundhaug JE, et al. Hydroxyethyl Starch (130 kD) Inhibits Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling Pathways in Rat Lungs Challenged with Lipopolysaccharide. Anesth Analg. 2011;113:112–119. - PubMed
-
- Churg A, Muller NL, Silva CI, Wright JL. Acute exacerbation (acute lung injury of unknown cause) in UIP and other forms of fibrotic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:277–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

