Unfolding visual lexical decision in time
- PMID: 22563419
- PMCID: PMC3338539
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035932
Unfolding visual lexical decision in time
Abstract
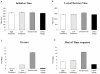
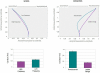
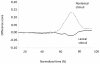
Visual lexical decision is a classical paradigm in psycholinguistics, and numerous studies have assessed the so-called "lexicality effect" (i.e., better performance with lexical than non-lexical stimuli). Far less is known about the dynamics of choice, because many studies measured overall reaction times, which are not informative about underlying processes. To unfold visual lexical decision in (over) time, we measured participants' hand movements toward one of two item alternatives by recording the streaming x,y coordinates of the computer mouse. Participants categorized four kinds of stimuli as "lexical" or "non-lexical:" high and low frequency words, pseudowords, and letter strings. Spatial attraction toward the opposite category was present for low frequency words and pseudowords. Increasing the ambiguity of the stimuli led to greater movement complexity and trajectory attraction to competitors, whereas no such effect was present for high frequency words and letter strings. Results fit well with dynamic models of perceptual decision-making, which describe the process as a competition between alternatives guided by the continuous accumulation of evidence. More broadly, our results point to a key role of statistical decision theory in studying linguistic processing in terms of dynamic and non-modular mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
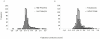

References
-
- Pagliuca G, Arduino LS, Barca L, Burani C. Fully transparent orthography, yet lexical reading aloud: The lexicality effect in Italian. Language and Cognitive Processes. 2008;23:422–433.
-
- Barca L, Bello A, Volterra V, Burani C. Lexical-semantic reading in a shallow orthography: evidence from a girl with Williams Syndrome. Reading and Writing. 2010;23:569–588.
-
- Barca L, Castrataro M, Rinaldi P, Caselli M. Written language processing in hearing and deaf. 2011. Poster presented at the ESCOP Conference, San Sebastian.
-
- Cisek P, Kalaska JF. Neural Mechanisms for Interacting with a World Full of Action Choices. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2010;33:269–298. - PubMed
-
- Gold J, Shadlen M. Neural computations that underlie decisions about sensory stimuli. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 2001;5:10–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

