HTR1A a novel type 1 diabetes susceptibility gene on chromosome 5p13-q13
- PMID: 22563461
- PMCID: PMC3341376
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035439
HTR1A a novel type 1 diabetes susceptibility gene on chromosome 5p13-q13
Abstract
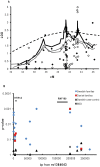
Background: We have previously performed a genome-wide linkage study in Scandinavian Type 1 diabetes (T1D) families. In the Swedish families, we detected suggestive linkage (LOD≤2.2) to the chromosome 5p13-q13 region. The aim of our study was to investigate the linked region in search for possible T1D susceptibility genes.
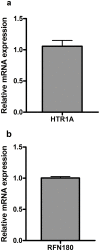
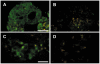
Methodology/principal findings: Microsatellites were genotyped in the Scandinavian families to fine-map the previously linked region. Further, SNPs were genotyped in Swedish and Danish families as well as Swedish sporadic cases. In the Swedish families we detected genome-wide significant linkage to the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A (HTR1A) gene (LOD 3.98, p<9.8×10(-6)). Markers tagging two separate genes; the ring finger protein 180 (RNF180) and HTR1A showed association to T1D in the Swedish and Danish families (p<0.002, p<0.001 respectively). The association was not confirmed in sporadic cases. Conditional analysis indicates that the primary association was to HTR1A. Quantitative PCR show that transcripts of both HTR1A and RNF180 are present in human islets of Langerhans. Moreover, immunohistochemical analysis confirmed the presence of the 5-HTR1A protein in isolated human islets of Langerhans as well as in sections of human pancreas.
Conclusions: We have identified and confirmed the association of both HTR1A and RFN180, two genes in high linkage disequilibrium (LD) to T1D in two separate family materials. As both HTR1A and RFN180 were expressed at the mRNA level and HTR1A as protein in human islets of Langerhans, we suggest that HTR1A may affect T1D susceptibility by modulating the initial autoimmune attack or either islet regeneration, insulin release, or both.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Group DP. Incidence and trends of childhood Type 1 diabetes worldwide 1990–1999. Diabet Med. 2006;23:857–866. - PubMed
-
- Patterson CC DG, Gyurus E, Green A, Soltesz G EURODIAB Study Group. Incidence trends for childhood type 1 diabetes in Europe during 1989–2003 and predicted new cases 2005–2020: a multicentre prospective registration study. Lancet. 2009;373:2027–2033. - PubMed
-
- Jensen RA GL, Törn C, Landin-Olsson M, Karlsson FA, Palmer JP, et al. Multiple factors affect the loss of measurable C-peptide over 6 years in newly diagnosed 15- to 35-year-old diabetic subjects. J Diabetes Complications. 2007;21:205–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

