Serum chitotriosidase activity in pulmonary tuberculosis: response to treatment and correlations with clinical parameters
- PMID: 22563552
- PMCID: PMC3339297
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2012.32.3.184
Serum chitotriosidase activity in pulmonary tuberculosis: response to treatment and correlations with clinical parameters
Abstract
Background: Chitotriosidase is an accepted marker of macrophage activation. In this study, we investigated serum chitotriosidase levels in pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB).
Methods: Forth-two patients with PTB and 30 healthy subjects were enrolled in the study. The radiological extent of PTB, radiological sequela after treatment, and the degree of smear positivity were assessed. Chitotriosidase levels were measured by a fluorometric method.
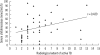
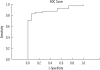
Results: The serum chitotriosidase levels of the PTB patients were significantly higher than those of the control subjects (39.73±24.97 vs. 9.63±4.55 nmol/mL/h, P<0.001). After completion of the standard 6-month antituberculous treatment, chitotriosidase levels in PTB patients significantly decreased (10.47±4.54 nmol/mL/h, P<0.001). Chitotriosidase levels correlated significantly with the radiological extent of PTB, degree of smear positivity, and post-treatment radiological sequela score (r=0.439, r=0.449, and r=0.337, respectively).
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that serum chitotriosidase levels increase in PTB; therefore, chitotriosidase can be used as a marker of disease activity, severity, and response to treatment.
Keywords: Chitotriosidase; Lung; Tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



References
-
- Di Rosa M, Musumeci M, Scuto A, Musumeci S, Malaguarnera L. Effect of interferon-γ, interleukin-10, lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor-α on chitotriosidase synthesis in human macrophages. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2005;43:499–502. - PubMed
-
- Michelakakis H, Dimitriou E, Labadaridis I. The expanding spectrum of disorders with elevated plasma chitotriosidase activity: an update. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2004;27:705–706. - PubMed
-
- Bargagli E, Maggiorelli C, Rottoli P. Human chitotriosidase: a potential new marker of sarcoidosis severity. Respiration. 2008;76:234–238. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

