Discovery of the first irreversible small molecule inhibitors of the interaction between the vitamin D receptor and coactivators
- PMID: 22563729
- PMCID: PMC3364162
- DOI: 10.1021/jm300460c
Discovery of the first irreversible small molecule inhibitors of the interaction between the vitamin D receptor and coactivators
Abstract
The vitamin D receptor (VDR) is a nuclear hormone receptor that regulates cell proliferation, cell differentiation, and calcium homeostasis. The receptor is activated by vitamin D analogues that induce the disruption of VDR-corepressor binding and promote VDR-coactivator interactions. The interactions between VDR and coregulators are essential for VDR-mediated transcription. Small molecule inhibition of VDR-coregulator binding represents an alternative method to the traditional ligand-based approach in order to modulate the expression of VDR target genes. A high throughput fluorescence polarization screen that quantifies the inhibition of binding between VDR and a fluorescently labeled steroid receptor coactivator 2 peptide was applied to discover the new small molecule VDR-coactivator inhibitors, 3-indolylmethanamines. Structure-activity relationship studies with 3-indolylmethanamine analogues were used to determine their mode of VDR-binding and to produce the first VDR-selective and irreversible VDR-coactivator inhibitors with the ability to regulate the transcription of the human VDR target gene TRPV6.
Figures



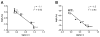







References
-
- Brumbaugh PF, Haussler MR. 1 Alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol receptors in intestine. I. Association of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol with intestinal mucosa chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1974;249:1251–1257. - PubMed
-
- Jurutka PW, Whitfield GK, Hsieh JC, Thompson PD, Haussler CA, Haussler MR. Molecular nature of the vitamin D receptor and its role in regulation of gene expression. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2001;2:203–216. - PubMed
-
- Feldman D, Pike JW, Glorieux FH. Vitamin D. 2. 1–2 Elsevier; Burlington: 2005.
-
- Yamada S, Shimizu M, Yamamoto K. Vitamin D receptor. Endocr Dev. 2003;6:50–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

