Viral disruption of the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 22564250
- PMCID: PMC3367119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2012.03.009
Viral disruption of the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
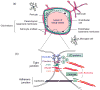
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) provides significant protection against microbial invasion of the brain. However, the BBB is not impenetrable, and mechanisms by which viruses breach it are becoming clearer. In vivo and in vitro model systems are enabling identification of host and viral factors contributing to breakdown of the unique BBB tight junctions. Key mechanisms of tight junction damage from inside and outside cells are disruption of the actin cytoskeleton and matrix metalloproteinase activity, respectively. Viral proteins acting in BBB disruption are described for HIV-1, currently the most studied encephalitic virus; other viruses are also discussed.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007.
-
- Salinas S, et al. A hitchhiker’s guide to the nervous system: the complex journey of viruses and toxins. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8:645–655. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, et al. Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;37:13–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

