Quantitative DNA methylation analysis identifies a single CpG dinucleotide important for ZAP-70 expression and predictive of prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 22564988
- PMCID: PMC3397783
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2011.39.3090
Quantitative DNA methylation analysis identifies a single CpG dinucleotide important for ZAP-70 expression and predictive of prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
Purpose: Increased ZAP-70 expression predicts poor prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Current methods for accurately measuring ZAP-70 expression are problematic, preventing widespread application of these tests in clinical decision making. We therefore used comprehensive DNA methylation profiling of the ZAP-70 regulatory region to identify sites important for transcriptional control.
Patients and methods: High-resolution quantitative DNA methylation analysis of the entire ZAP-70 gene regulatory regions was conducted on 247 samples from patients with CLL from four independent clinical studies.
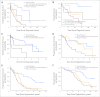
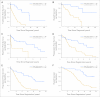
Results: Through this comprehensive analysis, we identified a small area in the 5' regulatory region of ZAP-70 that showed large variability in methylation in CLL samples but was universally methylated in normal B cells. High correlation with mRNA and protein expression, as well as activity in promoter reporter assays, revealed that within this differentially methylated region, a single CpG dinucleotide and neighboring nucleotides are particularly important in ZAP-70 transcriptional regulation. Furthermore, by using clustering approaches, we identified a prognostic role for this site in four independent data sets of patients with CLL using time to treatment, progression-free survival, and overall survival as clinical end points.
Conclusion: Comprehensive quantitative DNA methylation analysis of the ZAP-70 gene in CLL identified important regions responsible for transcriptional regulation. In addition, loss of methylation at a specific single CpG dinucleotide in the ZAP-70 5' regulatory sequence is a highly predictive and reproducible biomarker of poor prognosis in this disease. This work demonstrates the feasibility of using quantitative specific ZAP-70 methylation analysis as a relevant clinically applicable prognostic test in CLL.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, et al. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;94:1848–1854. - PubMed
-
- Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;94:1840–1847. - PubMed
-
- Zenz T, Mertens D, Küppers R, et al. From pathogenesis to treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:37–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

