PRC2 during vertebrate organogenesis: a complex in transition
- PMID: 22565092
- PMCID: PMC3374057
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.04.030
PRC2 during vertebrate organogenesis: a complex in transition
Abstract
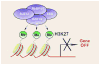
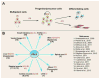
During organogenesis, tissues expand in size and eventually acquire consistent ratios of cells with dazzling diversity in morphology and function. During this process progenitor cells exit the cell cycle and execute differentiation programs through extensive genetic reprogramming that involves the silencing of proliferation genes and the activation of differentiation genes in a step-wise temporal manner. Recent years have witnessed expansion in our understanding of the epigenetic mechanisms that contribute to cellular differentiation and maturation during organ development, as this is a crucial step toward advancing regenerative therapy research for many intractable disorders. Among such epigenetic programs, the developmental roles of the polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), a chromatin remodeling complex that mediates silencing of gene expression, have been under intensive examination. This review summarizes recent findings of how PRC2 functions to regulate the transition from proliferation to differentiation during organogenesis and discusses some aspects of the remaining questions associated with its regulation and mechanisms of action.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Akasaka T, Kanno M, Balling R, Mieza MA, Taniguchi M, Koseki H. A role for mel-18, a Polycomb group-related vertebrate gene, during theanteroposterior specification of the axial skeleton. Development. 1996;122:1513–1522. - PubMed
-
- Akizu N, Estaras C, Guerrero L, Marti E, Martinez-Balbas MA. H3K27me3 regulates BMP activity in developing spinal cord. Development. 2010;137:2915–2925. - PubMed
-
- Alexander T, Nolte C, Krumlauf R. Hox genes and segmentation of the hindbrain and axial skeleton. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009;25:431–456. - PubMed
-
- Aoki R, Chiba T, Miyagi S, Negishi M, Konuma T, Taniguchi H, Ogawa M, Yokosuka O, Iwama A. The polycomb group gene product Ezh2 regulates proliferation and differentiation of murine hepatic stem/progenitor cells. J Hepatol. 2010;52:854–863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

