Adult Langerhans cells derive predominantly from embryonic fetal liver monocytes with a minor contribution of yolk sac-derived macrophages
- PMID: 22565823
- PMCID: PMC3371735
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20120340
Adult Langerhans cells derive predominantly from embryonic fetal liver monocytes with a minor contribution of yolk sac-derived macrophages
Abstract
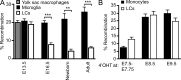
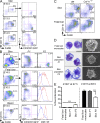
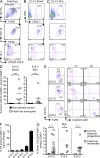
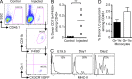
Langerhans cells (LCs) are the dendritic cells (DCs) of the epidermis, forming one of the first hematopoietic lines of defense against skin pathogens. In contrast to other DCs, LCs arise from hematopoietic precursors that seed the skin before birth. However, the origin of these embryonic precursors remains unclear. Using in vivo lineage tracing, we identify a first wave of yolk sac (YS)-derived primitive myeloid progenitors that seed the skin before the onset of fetal liver hematopoiesis. YS progenitors migrate to the embryo proper, including the prospective skin, where they give rise to LC precursors, and the brain rudiment, where they give rise to microglial cells. However, in contrast to microglia, which remain of YS origin throughout life, YS-derived LC precursors are largely replaced by fetal liver monocytes during late embryogenesis. Consequently, adult LCs derive predominantly from fetal liver monocyte-derived cells with a minor contribution of YS-derived cells. Altogether, we establish that adult LCs have a dual origin, bridging early embryonic and late fetal myeloid development.
Figures

References
-
- Bogunovic M., Ginhoux F., Wagers A., Loubeau M., Isola L.M., Lubrano L., Najfeld V., Phelps R.G., Grosskreutz C., Scigliano E., et al. 2006. Identification of a radio-resistant and cycling dermal dendritic cell population in mice and men. J. Exp. Med. 203:2627–2638 10.1084/jem.20060667 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Breathnach A.S., Silvers W.K., Smith J., Heyner S. 1968. Langerhans cells in mouse skin experimentally deprived of its neural crest component. J. Invest. Dermatol. 50:147–160 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI080884/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI080884/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA026504/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL086899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA112100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI095611/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA026504/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA032551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA32551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA26504/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

