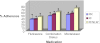Medication adherence among Latino and non-Latino white children with asthma
- PMID: 22566417
- PMCID: PMC3362901
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2011-1391
Medication adherence among Latino and non-Latino white children with asthma
Abstract
Objective: Latino children of Caribbean descent remain at high risk for poorly controlled asthma. Controller medications improve asthma control; however, medication adherence remains suboptimal, particularly among minorities. This study assessed socioeconomic, family-based, and parent factors in medication adherence among children with asthma from Rhode Island (RI; Latino and non-Latino white [NLW]) and Puerto Rico.
Methods: Data collection occurred as part of a multicenter study of asthma disparities. Our sample included children (ages 7-16) prescribed objectively monitored controller medications (n = 277; 80 island Puerto Rico, 114 RI Latino, 83 RI NLW). Parents completed questionnaires regarding family background and beliefs about medications. Families participated in an interview regarding asthma management. Multilevel analyses (maximum likelihood estimates) accounting for children being nested within site and ethnic group assessed the contribution of social context, family, and parent variables to medication adherence.
Results: Medication adherence differed by ethnic group (F(2, 271) = 7.46, P < .01), with NLW families demonstrating the highest levels of adherence. Multilevel models indicated that parental beliefs about medication necessity and family organization regarding medication use were significant predictors of adherence, even for families below the poverty threshold. With family factors in the model, a substantial improvement in model fit occurred (Akaike Information Criterion change of 103.45).
Conclusions: Adherence to controller medications was lower among Latino children in our sample. Targeted interventions that capitalize on existing family resources, emphasize structure, and address parental beliefs about the importance of medications may be of benefit to families from different cultural backgrounds.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Asthma Prevalence, Health Care Use, and Mortality, 2002. Hyattsville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2004
-
- Bender B, Wamboldt FS, O'Connor SL, Rand C, Szefler S, Milgrom H. Measurements of children's asthma medication by self report, mother report, canister weight, and Doser CT. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000;85(5):416–481 - PubMed
-
- McNally KA, Rohan J, Schluchter M, et al. Adherence to combined montelukast and fluticasone treatment in economically disadvantaged African American youth with asthma. J Asthma. 2009;46(9):921–927 - PubMed
-
- Burgess SW, Sly PD, Morawska A, Devadason SG. Assessing adherence and factors associated with adherence in young children with asthma. Respirology. 2008;13(4):559–563 - PubMed
-
- Ortega AN, Belanger KD, Paltiel AD, Horwitz SM, Bracken MB, Leaderer BP. Use of health services by insurance status among children with asthma. Med Care. 2001;39(10):1065–1074 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous