Management of symptomatic venous aneurysm
- PMID: 22566766
- PMCID: PMC3329879
- DOI: 10.1100/2012/386478
Management of symptomatic venous aneurysm
Abstract
Venous aneurysms (VAs) have been described in quite of all the major veins. They represent uncommon events but often life-threatening because of pulmonary or paradoxical embolism. We describe our twelve patients' series with acute pulmonary emboli due to venous aneurysm thrombosis. Our experience underlines the importance of a multilevel case-by-case approach and the immediate venous lower limbs duplex scan evaluation in pulmonary embolism events. Our data confirm that anticoagulant alone is not effective in preventing pulmonary embolism. We believe that all the VAs of the deep venous system of the extremities should be treated with surgery as well as symptomatic superficial venous aneurysm. A simple excision can significantly improve symptoms and prevent pulmonary embolism.
Figures

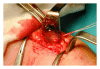

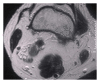


References
-
- Dahl JR, Freed TA, Burke MF. Popliteal vein aneurysm with recurrent pulmonary thromboemboli. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1976;236(22):2531–2532. - PubMed
-
- McDevitt DT, Lohr JM, Martin KD, Welling RE, Sampson MG. Bilateral popliteal vein aneurysms. Annals of Vascular Surgery. 1993;7(3):282–286. - PubMed
-
- Maleti O, Lugli M, Collura M. Anévrysmes veineux poplités: expérience personnelle. Phlebologie. 1997;50:53–59.
-
- Pascarella L, Al-Tuwaijri M, Bergan JJ, Mekenas LM. Lower extremity superficial venous aneurysms. Annals of Vascular Surgery. 2005;19(1):69–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

