Activation of natural killer cells during microbial infections
- PMID: 22566877
- PMCID: PMC3342047
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2011.00088
Activation of natural killer cells during microbial infections
Abstract
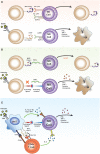
Natural killer (NK) cells are large granular lymphocytes that express a diverse array of germline encoded inhibitory and activating receptors for MHC Class I and Class I-like molecules, classical co-stimulatory ligands, and cytokines. The ability of NK cells to be very rapidly activated by inflammatory cytokines, to secrete effector cytokines, and to kill infected or stressed host cells, suggests that they may be among the very early responders during infection. Recent studies have also identified a small number of pathogen-derived ligands that can bind to NK cell surface receptors and directly induce their activation. Here we review recent studies that have begun to elucidate the various pathways by which viral, bacterial, and parasite pathogens activate NK cells. We also consider two emerging themes of NK cell-pathogen interactions, namely their contribution to adaptive immune responses and their potential to take on regulatory and immunomodulatory functions.
Keywords: NK cells; activation; bacteria; infection; parasites; viruses.
Figures



References
-
- Ahlenstiel G., Titerence R. H., Koh C., Edlich B., Feld J. J., Rotman Y., Ghany M. G., Hoofnagle J. H., Liang T. J., Heller T., Rehermann B. (2010). Natural killer cells are polarized toward cytotoxicity in chronic hepatitis C in an interferon-alfa-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 138, 325–335 e321–32210.1016/S0016-5085(10)62928-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Algarra I., Ortega E., Serrano M. J., Alvarez de Cienfuegos G., Gaforio J. J. (2002). Suppression of splenic macrophage Candida albicans phagocytosis following in vivo depletion of natural killer cells in immunocompetent BALB/c mice and T-cell-deficient nude mice. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 33, 159–16310.1111/j.1574-695X.2002.tb00586.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alter G., Jost S., Rihn S., Reyor L. L., Nolan B. E., Ghebremichael M., Bosch R., Altfeld M., Lauer G. M. (2011b). Reduced frequencies of NKp30+NKp46+, CD161+, and NKG2D+ NK cells in acute HCV infection may predict viral clearance. J. Hepatol. 55, 278–28810.1016/j.jhep.2010.11.030 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

