Do anti-angiogenic VEGF (VEGFxxxb) isoforms exist? A cautionary tale
- PMID: 22567098
- PMCID: PMC3342274
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035231
Do anti-angiogenic VEGF (VEGFxxxb) isoforms exist? A cautionary tale
Abstract
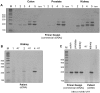
Splicing of the human vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) gene has been reported to generate angiogenic (VEGFxxx) and anti-angiogenic (VEGFxxxb) isoforms. Corresponding VEGFxxxb isoforms have also been reported in rat and mouse. We examined VEGFxxxb expression in mouse fibrosarcoma cell lines expressing all or individual VEGF isoforms (VEGF120, 164 or 188), grown in vitro and in vivo, and compared results with those from normal mouse and human tissues. Importantly, genetic construction of VEGF164 and VEGF188 expressing fibrosarcomas, in which exon 7 is fused to the conventional exon 8, precludes VEGFxxxb splicing from occurring. Thus, these two fibrosarcoma cell lines provided endogenous negative controls. Using RT-PCR we show that primers designed to simultaneously amplify VEGFxxx and VEGFxxxb isoforms amplified only VEGFxxx variants in both species. Moreover, only VEGFxxx species were generated when mouse podocytes were treated with TGFβ-1, a reported activator of VEGFxxxb splice selection in human podocytes. A VEGF164/120 heteroduplex species was identified as a PCR artefact, specifically in mouse. VEGFxxxb isoform-specific PCR did amplify putative VEGFxxxb species in mouse and human tissues, but unexpectedly also in VEGF188 and VEGF164 fibrosarcoma cells and tumours, where splicing to produce true VEGFxxxb isoforms cannot occur. Moreover, these products were only consistently generated using reverse primers spanning more than 5 bases across the 8b/7 or 8b/5 splice junctions. Primer annealing to VEGFxxx transcripts and amplification of exon 8b primer 'tails' explained the artefactual generation of VEGFxxxb products, since the same products were generated when the PCR reactions were performed with cDNA from VEGF164/VEGF188 'knock-in' vectors used in the generation of single VEGF isoform-expressing transgenic mice from which the fibrosarcoma lines were developed. Collectively, our results highlight important pitfalls in data interpretation associated with detecting VEGFxxxb isoforms using current methods, and demonstrate that anti-angiogenic isoforms are not commonly expressed in mouse or human tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


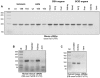
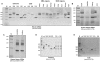

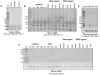
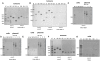

References
-
- Ferrara N. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in pathological angiogenesis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995;36:127–137. - PubMed
-
- Tomisawa M, Tokunaga T, Oshika Y, Tsuchida T, Fukushima Y, et al. Expression pattern of vascular endothelial growth factor isoform is closely correlated with tumour stage and vascularisation in renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 1999;35:133–137. - PubMed
-
- Lee YH, Tokunaga T, Oshika Y, Suto R, Yanagisawa K, et al. Cell-retained isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are correlated with poor prognosis in osteosarcoma. Eur J Cancer. 1999;35:1089–1093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

