Oral Candidiasis: Aiding in the Diagnosis of HIV-A Case Report
- PMID: 22567448
- PMCID: PMC3335721
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/929616
Oral Candidiasis: Aiding in the Diagnosis of HIV-A Case Report
Abstract
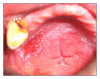
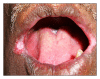
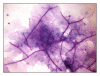
Opportunistic fungal infections account for a significant amount of morbidity associated with HIV disease. Candidiasis is the most common oral opportunistic infection affecting people with HIV infection or AIDS. It is considered as an important marker of immune suppression and may be the initial manifestation of the disease in about 10% of HIV-infected adults. We report a case of an apparently healthy 45-year-old male with oral candidiasis which proved to be the first indicator of HIV infection.
Figures
References
-
- McCarthy GM, Mackie ID, Koval J, Sandhu HS, Daley TD. Factors associated with increased frequency of HIV-related oral candidiasis. Journal of Oral Pathology and Medicine. 1991;20(7):332–336. - PubMed
-
- Sharma G, Pai KM, Suhas S, Ramapuram JT, Doshi D, Anup N. Oral manifestations in HIV/AIDS infected patients from India. Oral Diseases. 2006;12(6):537–542. - PubMed
-
- Van der Waal I, Schulten EA, Pindborg JJ. Oral manifestations of AIDS: an overview. International Dental Journal. 1991;41(1):3–8. - PubMed
-
- Ranganathan K, Reddy BVR, Kumarasamy N, Solomon S, Viswanathan R, Johnson NW. Oral lesions and conditions associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection in 300 south Indian patients. Oral Diseases. 2000;6(3):152–157. - PubMed
-
- Touyz L, Harel-Raviv M, Prosterman B, Gornitsky M. Candidal infection of the tongue together with candidal infection of the palate in patients with the human immunodeficiency virus. Quintessence International. 1996;27(2):89–92. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources