High-performance liquid chromatography assay for moxifloxacin in brain tissue and plasma: validation in a pharmacokinetic study in a murine model of cerebral listeriosis
- PMID: 22567560
- PMCID: PMC3335337
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/436349
High-performance liquid chromatography assay for moxifloxacin in brain tissue and plasma: validation in a pharmacokinetic study in a murine model of cerebral listeriosis
Abstract
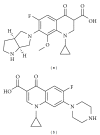
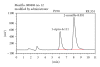
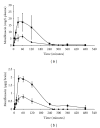
Moxifloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibacterial 8-methoxy-fluoroquinolone. In order to evaluate the pharmacokinetic properties of moxifloxacin in mouse plasma and brain tissue, we developed a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. This study was based on single-drug delivery, intravenously dosed in a central listeriosis murine model. The method employed a reversed-phase Lichrospher RP-18 with a precolumn (250 × 4.6 mm) and a mobile phase composed of a mixture of acetonitrile, methanol, and citric buffer (pH = 3.5) with sodium dodecyl sulfate and tetrabutylammonium bromide. Fluorescence detection was performed at an excitation wavelength of 290 nm and an emission wavelength of 550 nm. The relative standard deviation of intra- and inter-day assays was <10%. This validated method led to a short retention time (8.0 min) for moxifloxacin. The standard curves were linear from 5-250 μg/L in plasma and from 0.1-2.5 μg/g of brain tissue. The limits of quantification were 5 μg/L in plasma and 0.1 μg/g in brain tissue. The method enabled the detection of systemic antimicrobial in plasma and in CNS in Listeria-infected mice. Injected moxifloxacin passed through the encephalic barrier within a 30 to 60 min after injection time frame. Moxifloxacin pharmacokinetics are modeled in an infected model compared to control mice.
Figures
References
-
- Balfour JAB, Wiseman LR. Moxifloxacin. Drugs. 1999;57(3):363–374. - PubMed
-
- The Merck index. p. 1125, 2001.
-
- Goulet V, Marchetti P. Listeriosis in 225 non-pregnant patients in 1992: clinical aspects and outcome in relation to predisposing conditions. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases. 1996;28(4):367–374. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

