Highly Selective Hg (II) Ion Detection Based on Linear Blue-Shift of the Maximum Absorption Wavelength of Silver Nanoparticles
- PMID: 22567571
- PMCID: PMC3335303
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/856947
Highly Selective Hg (II) Ion Detection Based on Linear Blue-Shift of the Maximum Absorption Wavelength of Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
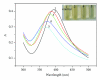
A new method of detecting Hg (II) ion with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) is developed in this contribution. When Hg (II) ions were added into AgNPs solution, the solution displayed rapid color change and blue shift of the maximum absorption wavelength (Δλ), which was in proportion to the Hg (II) ion concentration over the range of 2.0 × 10(-7)-6.0 × 10(-6) mol/L, with detection limit (3σ) of 6.6 × 10(-9 )mol/L. Under the same experimental conditions, other metal ions did not interfere. Thus, we propose a rapid, simple and highly selective method for detecting Hg (II) ion.
Figures






References
-
- Sekowski JW, Malkas LH, Wei Y, Hickey RJ. Mercuric ion inhibits the activity and fidelity of the human cell dna synthesome. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 1997;145(2):268–276. - PubMed
-
- Manganiello L, Ríos A, Valcárcel M. A method for screening total mercury in water using a flow injection system with piezoelectric detection. Analytical Chemistry. 2002;74(4):921–925. - PubMed
-
- Si S, Kotal A, Mandal TK. One-dimensional assembly of peptide-functionalized gold nanoparticles: an approach toward mercury ion sensing. Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 2007;111(3):1248–1255.
-
- Lee JS, Han MS, Mirkin CA. Colorimetric detection of mercuric ion (hg2+) in aqueous media using dna-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Angewandte Chemie. 2007;46(22):4093–4096. - PubMed
-
- Yu CJ, Cheng TL, Tseng WL. Effects of mn2+ on oligonucleotide-gold nanoparticle hybrids for colorimetric sensing of hg2+: improving colorimetric sensitivity and accelerating color change. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2009;25(1):204–210. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

