In vivo imaging of unstained tissues using long gradient index lens multiphoton endoscopic systems
- PMID: 22567597
- PMCID: PMC3342183
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.3.001077
In vivo imaging of unstained tissues using long gradient index lens multiphoton endoscopic systems
Abstract
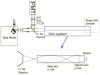
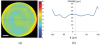
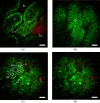
We characterize long (up to 285 mm) gradient index (GRIN) lens endoscope systems for multiphoton imaging. We fabricate a portable, rigid endoscope system suitable for imaging unstained tissues, potentially deep within the body, using a GRIN lens system of 1 mm diameter and 8 cm length. The portable device is capable of imaging a ~200 µm diameter field of view at 4 frames/s. The lateral and axial resolution in water is 0.85 µm and 7.4 µm respectively. In vivo images of unstained tissues in live, anesthetized rats using the portable device are presented. These results show great promise for GRIN endoscopy to be used clinically.
Keywords: (110.2760) Gradient-index lenses; (170.2150) Endoscopic imaging; (180.4315) Nonlinear microscopy.
Figures



References
-
- Lin S. J., Jee S. H., Kuo C. J., Wu R. J., Lin W. C., Chen J. S., Liao Y. H., Hsu C. J., Tsai T. F., Chen Y. F., Dong C. Y., “Discrimination of basal cell carcinoma from normal dermal stroma by quantitative multiphoton imaging,” Opt. Lett. 31(18), 2756–2758 (2006). 10.1364/OL.31.002756 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Skala M. C., Squirrell J. M., Vrotsos K. M., Eickhoff J. C., Gendron-Fitzpatrick A., Eliceiri K. W., Ramanujam N., “Multiphoton microscopy of endogenous fluorescence differentiates normal, precancerous, and cancerous squamous epithelial tissues,” Cancer Res. 65(4), 1180–1186 (2005). 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3031 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
