Interkingdom signaling: integration, conformation, and orientation of N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones in supported lipid bilayers
- PMID: 22568488
- PMCID: PMC3388113
- DOI: 10.1021/la301241s
Interkingdom signaling: integration, conformation, and orientation of N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones in supported lipid bilayers
Abstract
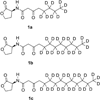
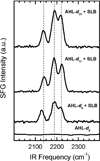
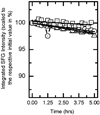
N-Acyl-L-homoserine lactones (AHLs) are small cell-to-cell signaling molecules involved in the regulation of population density and local gene expression in microbial communities. Recent evidence shows that contact of this signaling system, usually referred to as quorum sensing, to living eukaryotes results in interactions of AHL with host cells in a process termed "interkingdom signaling". So far details of this process and the binding site of the AHLs remain unknown; both an intracellular and a membrane-bound receptor seem possible, the first of which requires passage through the cell membrane. Here, we used sum-frequency-generation (SFG) spectroscopy to investigate the integration, conformation, orientation, and translocation of deuterated N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones (AHL-d(n)) with varying chain length (8, 12, and 14 C atoms) in lipid bilayers consisting of a 1:1 mixture of POPC:POPG supported on SiO(2) substrates (prepared by vesicle fusion). We found that all AHL-d(n) derivatives are well-ordered within the supported lipid bilayer (SLB) in a preferentially all-trans conformation of the deuterated alkyl chain and integrated into the upper leaflet of the SLB with the methyl terminal groups pointing downward. For the bilayer system described above, no flip-flop of AHL-d(n) from the upper leaflet to the lower one could be observed. Spectral assignments and interpretations were further supported by Fourier transform infrared and Raman spectroscopy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Deuterium-labelled N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones (AHLs)--inter-kingdom signalling molecules--synthesis, structural studies, and interactions with model lipid membranes.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012 Apr;403(2):473-82. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-5839-4. Epub 2012 Feb 26. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22367286
-
Bacillus megaterium CYP102A1 oxidation of acyl homoserine lactones and acyl homoserines.Biochemistry. 2007 Dec 18;46(50):14429-37. doi: 10.1021/bi701945j. Epub 2007 Nov 20. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 18020460
-
Interactions of Bacterial Quorum Sensing Signals with Model Lipid Membranes: Influence of Acyl Tail Structure on Multiscale Response.Langmuir. 2021 Oct 19;37(41):12049-12058. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c01825. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Langmuir. 2021. PMID: 34606725 Free PMC article.
-
Quenching of acyl-homoserine lactone-dependent quorum sensing by enzymatic disruption of signal molecules.Acta Biochim Pol. 2009;56(1):1-16. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Acta Biochim Pol. 2009. PMID: 19287806 Review.
-
Heterocyclic Chemistry Applied to the Design of N-Acyl Homoserine Lactone Analogues as Bacterial Quorum Sensing Signals Mimics.Molecules. 2021 Aug 24;26(17):5135. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175135. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tasting Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms: Human Neutrophils Express the Bitter Receptor T2R38 as Sensor for the Quorum Sensing Molecule N-(3-Oxododecanoyl)-l-Homoserine Lactone.Front Immunol. 2015 Jul 24;6:369. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00369. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26257736 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane vesicle-mediated bacterial communication.ISME J. 2017 Jun;11(6):1504-1509. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2017.13. Epub 2017 Mar 10. ISME J. 2017. PMID: 28282039 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane orientation of Gα(i)β(1)γ(2) and Gβ(1)γ(2) determined via combined vibrational spectroscopic studies.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Apr 3;135(13):5044-51. doi: 10.1021/ja3116026. Epub 2013 Mar 21. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23461393 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Fluid-Gel Phase Transition Induced Alamethicin Orientational Change Probed by Sum Frequency Generation Vibrational Spectroscopy.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2013 Aug 20;117(33):17039-17049. doi: 10.1021/jp4047215. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2013. PMID: 24124624 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular simulations of lipid membrane partitioning and translocation by bacterial quorum sensing modulators.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 9;16(2):e0246187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246187. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33561158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP. Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999;284(5418):1318–1322. - PubMed
-
- Krumbein WE, Paterson DM, Zavarzin GA. Fossil and recent biofilms : a natural history of life on Earth. Dordrecht; Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2003. p. xxi.p. 482.
-
- Costerton JW, Cheng KJ, Geesey GG, Ladd TI, Nickel JC, Dasgupta M, Marrie TJ. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1987;41:435–464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

