The testis-specific double bromodomain-containing protein BRDT forms a complex with multiple spliceosome components and is required for mRNA splicing and 3'-UTR truncation in round spermatids
- PMID: 22570411
- PMCID: PMC3424537
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks342
The testis-specific double bromodomain-containing protein BRDT forms a complex with multiple spliceosome components and is required for mRNA splicing and 3'-UTR truncation in round spermatids
Abstract
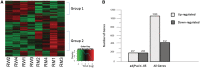
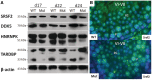
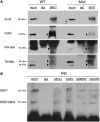
Members of the BET (bromodomain and extra terminal motif) family of proteins have been shown to be chromatin-interacting regulators of transcription. We previously generated a mutation in the testis-specific mammalian BET gene Brdt (bromodomain, testis-specific) that yields protein lacking the first bromodomain (BRDT(ΔBD1)) and observed disrupted spermiogenesis and male sterility. To determine whether BRDT(ΔBD1) protein results in altered transcription, we analyzed the transcriptomes of control versus Brdt(ΔBD1/ΔBD1) round spermatids. Over 400 genes showed statistically significant differential expression, and among the up-regulated genes, there was an enrichment of RNA splicing genes. Over 60% of these splicing genes had transcripts that lacked truncation of their 3'-untranslated region (UTR) typical of round spermatids. We selected four of these genes to characterize: Srsf2, Ddx5, Hnrnpk and Tardbp. The 3'-UTRs of Srsf2, Ddx5 and Hnrnpk mRNAs were longer in mutant round spermatids and resulted in reduced protein levels. Tardbp was transcriptionally up-regulated and a splicing shift toward the longer variant was observed. All four splicing proteins were found to complex with BRDT in control and mutant testes. We thus suggest that, along with modulating transcription, BRDT modulates gene expression as part of the splicing machinery. These modulations alter 3'-UTR processing in round spermatids; importantly, the BD1 is essential for these functions.
Figures


References
-
- Florence B, Faller DV. You bet-cha: a novel family of transcriptional regulators. Front. Biosci. 2001;6:D1008–D1018. - PubMed
-
- Kanno T, Kanno Y, Siegel RM, Jang MK, Lenardo MJ, Ozato K. Selective recognition of acetylated histones by bromodomain proteins visualized in living cells. Mol. Cell. 2004;13:33–43. - PubMed
-
- Moriniere J, Rousseaux S, Steuerwald U, Soler-Lopez M, Curtet S, Vitte AL, Govin J, Gaucher J, Sadoul K, Hart DJ, et al. Cooperative binding of two acetylation marks on a histone tail by a single bromodomain. Nature. 2009;461:664–668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

