Rapid incorporation kinetics and improved fidelity of a novel class of 3'-OH unblocked reversible terminators
- PMID: 22570423
- PMCID: PMC3424534
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks330
Rapid incorporation kinetics and improved fidelity of a novel class of 3'-OH unblocked reversible terminators
Abstract
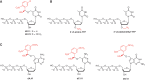
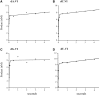
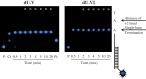
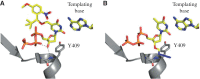
Recent developments of unique nucleotide probes have expanded our understanding of DNA polymerase function, providing many benefits to techniques involving next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies. The cyclic reversible termination (CRT) method depends on efficient base-selective incorporation of reversible terminators by DNA polymerases. Most terminators are designed with 3'-O-blocking groups but are incorporated with low efficiency and fidelity. We have developed a novel class of 3'-OH unblocked nucleotides, called Lightning Terminators™, which have a terminating 2-nitrobenzyl moiety attached to hydroxymethylated nucleobases. A key structural feature of this photocleavable group displays a 'molecular tuning' effect with respect to single-base termination and improved nucleotide fidelity. Using Therminator DNA polymerase, we demonstrate that these 3'-OH unblocked terminators exhibit superior enzymatic performance compared to two other reversible terminators, 3'-O-amino-TTP and 3'-O-azidomethyl-TTP. Lightning Terminators show maximum incorporation rates (k(pol)) that range from 35 to 45 nt/s, comparable to the fastest NGS chemistries, yet with catalytic efficiencies (k(pol)/K(D)) comparable to natural nucleotides. Pre-steady-state kinetic studies of thymidine analogs revealed that the major determinant for improved nucleotide selectivity is a significant reduction in k(pol) by >1000-fold over TTP misincorporation. These studies highlight the importance of structure-function relationships of modified nucleotides in dictating polymerase performance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improved nucleotide selectivity and termination of 3'-OH unblocked reversible terminators by molecular tuning of 2-nitrobenzyl alkylated HOMedU triphosphates.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Mar;39(6):e39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1293. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21227920 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated system for DNA sequencing by synthesis using novel nucleotide analogues.Acc Chem Res. 2010 Apr 20;43(4):551-63. doi: 10.1021/ar900255c. Acc Chem Res. 2010. PMID: 20121268 Free PMC article.
-
3'-O-modified nucleotides as reversible terminators for pyrosequencing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 16;104(42):16462-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707495104. Epub 2007 Oct 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17923668 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential sequencing by synthesis and the next-generation sequencing revolution.Trends Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;41(12):1565-1572. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2023.06.007. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Trends Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37482467 Review.
-
A reexamination of the nucleotide incorporation fidelity of DNA polymerases.Biochemistry. 2002 Aug 27;41(34):10571-6. doi: 10.1021/bi026021i. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12186540 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA polymerases drive DNA sequencing-by-synthesis technologies: both past and present.Front Microbiol. 2014 Jun 24;5:305. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00305. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25009536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Introducing a New Bond-Forming Activity in an Archaeal DNA Polymerase by Structure-Guided Enzyme Redesign.ACS Chem Biol. 2022 Jul 15;17(7):1924-1936. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00373. Epub 2022 Jul 1. ACS Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35776893 Free PMC article.
-
One-step enzymatic modification of RNA 3' termini using polymerase θ.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Apr 23;47(7):3272-3283. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz029. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30818397 Free PMC article.
-
The history and advances of reversible terminators used in new generations of sequencing technology.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2013 Feb;11(1):34-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2013.01.003. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23414612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enzymatic Synthesis of Vancomycin-Modified DNA.Molecules. 2022 Dec 15;27(24):8927. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248927. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36558056 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

