The homeodomain-containing transcription factors Arx and Pax4 control enteroendocrine subtype specification in mice
- PMID: 22570716
- PMCID: PMC3343025
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036449
The homeodomain-containing transcription factors Arx and Pax4 control enteroendocrine subtype specification in mice
Abstract
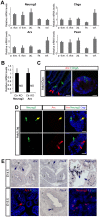
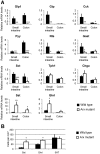
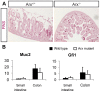
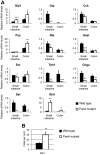
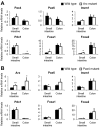
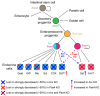
Intestinal hormones are key regulators of digestion and energy homeostasis secreted by rare enteroendocrine cells. These cells produce over ten different hormones including GLP-1 and GIP peptides known to promote insulin secretion. To date, the molecular mechanisms controlling the specification of the various enteroendocrine subtypes from multipotent Neurog3(+) endocrine progenitor cells, as well as their number, remain largely unknown. In contrast, in the embryonic pancreas, the opposite activities of Arx and Pax4 homeodomain transcription factors promote islet progenitor cells towards the different endocrine cell fates. In this study, we thus investigated the role of Arx and Pax4 in enteroendocrine subtype specification. The small intestine and colon of Arx- and Pax4-deficient mice were analyzed using histological, molecular, and lineage tracing approaches. We show that Arx is expressed in endocrine progenitors (Neurog3(+)) and in early differentiating (ChromograninA(-)) GLP-1-, GIP-, CCK-, Sct- Gastrin- and Ghrelin-producing cells. We noted a dramatic reduction or a complete loss of all these enteroendocrine cell types in Arx mutants. Serotonin- and Somatostatin-secreting cells do not express Arx and, accordingly, the differentiation of Serotonin cells was not affected in Arx mutants. However, the number of Somatostatin-expressing D-cells is increased as Arx-deficient progenitor cells are redirected to the D-cell lineage. In Pax4-deficient mice, the differentiation of Serotonin and Somatostatin cells is impaired, as well as of GIP and Gastrin cells. In contrast, the number of GLP-1 producing L-cells is increased concomitantly with an upregulation of Arx. Thus, while Arx and Pax4 are necessary for the development of L- and D-cells respectively, they conversely restrict D- and L-cells fates suggesting antagonistic functions in D/L cell allocation. In conclusion, these finding demonstrate that, downstream of Neurog3, the specification of a subset of enteroendocrine subtypes relies on both Arx and Pax4, while others depend only on Arx or Pax4.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Date Y, Kojima M, Hosoda H, Sawaguchi A, Mondal MS, et al. Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology. 2000;141:4255–4261. - PubMed
-
- Sakata I, Nakamura K, Yamazaki M, Matsubara M, Hayashi Y, et al. Ghrelin-producing cells exist as two types of cells, closed- and opened-type cells, in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Peptides. 2002;23:531–536. - PubMed
-
- Murphy KG, Bloom SR. Gut hormones and the regulation of energy homeostasis. Nature. 2006;444:854–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

