Epidemiology of gallbladder disease: cholelithiasis and cancer
- PMID: 22570746
- PMCID: PMC3343155
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2012.6.2.172
Epidemiology of gallbladder disease: cholelithiasis and cancer
Abstract
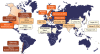
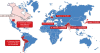
Diseases of the gallbladder are common and costly. The best epidemiological screening method to accurately determine point prevalence of gallstone disease is ultrasonography. Many risk factors for cholesterol gallstone formation are not modifiable such as ethnic background, increasing age, female gender and family history or genetics. Conversely, the modifiable risks for cholesterol gallstones are obesity, rapid weight loss and a sedentary lifestyle. The rising epidemic of obesity and the metabolic syndrome predicts an escalation of cholesterol gallstone frequency. Risk factors for biliary sludge include pregnancy, drugs like ceftiaxone, octreotide and thiazide diuretics, and total parenteral nutrition or fasting. Diseases like cirrhosis, chronic hemolysis and ileal Crohn's disease are risk factors for black pigment stones. Gallstone disease in childhood, once considered rare, has become increasingly recognized with similar risk factors as those in adults, particularly obesity. Gallbladder cancer is uncommon in developed countries. In the U.S., it accounts for only ~ 5,000 cases per year. Elsewhere, high incidence rates occur in North and South American Indians. Other than ethnicity and female gender, additional risk factors for gallbladder cancer include cholelithiasis, advancing age, chronic inflammatory conditions affecting the gallbladder, congenital biliary abnormalities, and diagnostic confusion over gallbladder polyps.
Keywords: Cholecystectomy; Gallbladder cancer; Gallbladder polyps; Gallstones.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Gracie WA, Ransohoff DF. The natural history of silent gallstones: the innocent gallstone is not a myth. N Engl J Med. 1982;307:798–800. - PubMed
-
- Shaffer EA. Epidemiology and risk factors for gallstone disease: has the paradigm changed in the 21st century? Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2005;7:132–140. - PubMed
-
- Kratzer W, Mason RA, Kächele V. Prevalence of gallstones in sonographic surveys worldwide. J Clin Ultrasound. 1999;27:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Pedersen G, Hoem D, Andrén-Sandberg A. Influence of laparoscopic cholecystectomy on the prevalence of operations for gallstones in Norway. Eur J Surg. 2002;168:464–469. - PubMed
-
- Schirmer BD, Winters KL, Edlich RF. Cholelithiasis and cholecystitis. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2005;15:329–338. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

