Comparison of xMAP and ELISA assays for detecting cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22571982
- PMCID: PMC3660971
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-2012-120082
Comparison of xMAP and ELISA assays for detecting cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
The best-studied biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease (AD) are the pathologically-linked cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) proteins amyloid-β 42 (Aβ(1-42)), total tau (t-tau), and tau phosphorylated on amino acid 181 (p-tau(181)). Many laboratories measure these proteins using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Multiplex xMAP Luminex is a semi-automated assay platform with reduced intra-sample variance, which could facilitate its use in CLIA-approved clinical laboratories. CSF concentrations of these three biomarkers reported using xMAP technology differ from those measured by the most commonly used ELISA, confounding attempts to compare results. To develop a model for converting between xMAP and ELISA levels of the three biomarkers, we analyzed CSF samples from 140 subjects (59 AD, 30 controls, 34 with mild cognitive impairment, and 17 with Parkinson's disease, including 1 with dementia). Log-transformation of ELISA and xMAP levels made the variance constant in all three biomarkers and improved the linear regression: t-tau concentrations were highly correlated (r = 0.94); p-tau(181) concentrations by ELISA can be better predicted using both the t-tau and p-tau(181) xMAP values (r = 0.96) as compared to p-tau(181) concentrations alone (r = 0.82); correlation of Aβ(1-42) concentrations was relatively weaker but still high (r = 0.77). Among all six protein/assay combinations, xMAP Aβ(1-42) had the best accuracy for diagnostic classification (88%) between AD and control subjects. In conclusion, our study demonstrates that multiplex xMAP is an appropriate assay platform providing results that can be correlated with research-based ELISA values, facilitating the incorporation of this diagnostic biomarker into routine clinical practice.
Figures

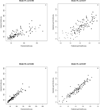
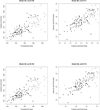
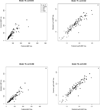


References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2011 Alzheimer’s Disease:Facts and Figures. 2011.
-
- McKhann GM, Albert MS, Grossman M, Miller B, Dickson D, Trojanowski JQ. Clinical and pathological diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia: report of the Work Group on Frontotemporal Dementia and Pick’s Disease. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:1803–1809. - PubMed
-
- Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Dekosky ST, Barberger-Gateau P, Cummings J, Delacourte A, Galasko D, Gauthier S, Jicha G, Meguro K, O’brien J, Pasquier F, Robert P, Rossor M, Salloway S, Stern Y, Visser PJ, Scheltens P. Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: revising the NINCDSADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:734–746. - PubMed
-
- Clark CM, Xie S, Chittams J, Ewbank D, Peskind E, Galasko D, Morris JC, McKeel DW, Farlow M, Weitlauf SL, Quinn J, Kaye J, Knopman D, Arai H, Doody RS, DeCarli C, Leight S, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Cerebrospinal fluid tau and beta-amyloid: how well do these biomarkers reflect autopsyconfirmed dementia diagnoses? Arch Neurol. 2003;60:1696–1702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

