Alanyl-tRNA synthetase mutation in a family with dominant distal hereditary motor neuropathy
- PMID: 22573628
- PMCID: PMC3359507
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182574f8f
Alanyl-tRNA synthetase mutation in a family with dominant distal hereditary motor neuropathy
Abstract
Objective: To identify a new genetic cause of distal hereditary motor neuropathy (dHMN), which is also known as a variant of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT), in a Chinese family.
Methods: We investigated a Chinese family with dHMN clinically, electrophysiologically, and genetically. We screened for the mutations of 28 CMT or related pathogenic genes using an originally designed microarray resequencing DNA chip.
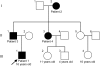
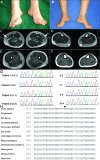
Results: Investigation of the family history revealed an autosomal dominant transmission pattern. The clinical features of the family included mild weakness and wasting of the distal muscles of the lower limb and foot deformity, without clinical sensory involvement. Electrophysiologic studies revealed motor neuropathy. MRI of the lower limbs showed accentuated fatty infiltration of the gastrocnemius and vastus lateralis muscles. All 4 affected family members had a heterozygous missense mutation c.2677G>A (p.D893N) of alanyl-tRNA synthetase (AARS), which was not found in the 4 unaffected members and control subjects.
Conclusion: An AARS mutation caused dHMN in a Chinese family. AARS mutations result in not only a CMT phenotype but also a dHMN phenotype.
Figures
References
-
- Harding AE. Inherited neuronal atrophy and degeneration predominantly of lower motor neurons. In: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, eds. Peripheral Neuropathy. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1993
-
- Drew AP, Blair IP, Nicholson GA. Molecular genetics and mechanisms of disease in distal hereditary motor neuropathies: insights directing future genetic studies. Curr Mol Med 2011;11:650–665 - PubMed
-
- Irobi J, Van Impe K, Seeman P, et al. Hot-spot residue in small heat-shock protein 22 causes distal motor neuropathy. Nat Genet 2004;36:597–601 - PubMed
-
- Houlden H, Laura M, Wavrant-De Vrièze F, et al. Mutations in the HSP27 (HSPB1) gene cause dominant, recessive, and sporadic distal HMN/CMT type 2. Neurology 2008;71:1660–1668 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
