Transglutaminase inhibition protects against oxidative stress-induced neuronal death downstream of pathological ERK activation
- PMID: 22573678
- PMCID: PMC3444816
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3353-11.2012
Transglutaminase inhibition protects against oxidative stress-induced neuronal death downstream of pathological ERK activation
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2012 Aug 8;32(32):11157
Abstract
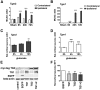
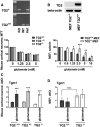
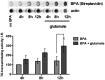
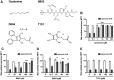
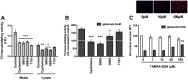
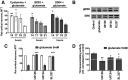
Molecular deletion of transglutaminase 2 (TG2) has been shown to improve function and survival in a host of neurological conditions including stroke, Huntington's disease, and Parkinson's disease. However, unifying schemes by which these cross-linking or polyaminating enzymes participate broadly in neuronal death have yet to be presented. Unexpectedly, we found that in addition to TG2, TG1 gene expression level is significantly induced following stroke in vivo or due to oxidative stress in vitro. Forced expression of TG1 or TG2 proteins is sufficient to induce neuronal death in Rattus norvegicus cortical neurons in vitro. Accordingly, molecular deletion of TG2 alone is insufficient to protect Mus musculus neurons from oxidative death. By contrast, structurally diverse inhibitors used at concentrations that inhibit TG1 and TG2 simultaneously are neuroprotective. These small molecules inhibit increases in neuronal transamidating activity induced by oxidative stress; they also protect neurons downstream of pathological ERK activation when added well after the onset of the death stimulus. Together, these studies suggest that multiple TG isoforms, not only TG2, participate in oxidative stress-induced cell death signaling; and that isoform nonselective inhibitors of TG will be most efficacious in combating oxidative death in neurological disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Akimov SS, Belkin AM. Opposing roles of Ras/Raf oncogenes and the MEK1/ERK signaling module in regulation of expression and adhesive function of surface transglutaminase. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:35609–35619. - PubMed
-
- Bailey CD, Johnson GV. The protective effects of cystamine in the R6/2 Huntington's disease mouse involve mechanisms other than the inhibition of tissue transglutaminase. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27:871–879. - PubMed
-
- Borrell-Pagès M, Canals JM, Cordelières FP, Parker JA, Pineda JR, Grange G, Bryson EA, Guillermier M, Hirsch E, Hantraye P, Cheetham ME, Néri C, Alberch J, Brouillet E, Saudou F, Humbert S. Cystamine and cysteamine increase brain levels of BDNF in Huntington disease via HSJ1b and transglutaminase. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:1410–1424. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
