Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus induces interleukin-15 through the NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 22573868
- PMCID: PMC3416278
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00177-12
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus induces interleukin-15 through the NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
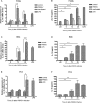
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) mainly infects macrophages/dendritic cells and modulates cytokine expression in these cells. Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a pleiotropic cytokine involved in wide range of biological activities. It has been shown to be essential for the generation, activation, and proliferation of NK and NKT cells and for the survival and activation of CD8(+) effector and memory T cells. In this study, we discovered that PRRSV infection upregulated IL-15 production at both the mRNA and protein levels in porcine alveolar macrophages (PAMs), blood monocyte-derived macrophages (BMo), and monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DCs). We subsequently demonstrated that the NF-κB signaling pathway was essential for PRRSV infection-induced IL-15 production. First, addition of an NF-κB inhibitor drastically reduced PRRSV infection-induced IL-15 production. We then found that NF-κB was indeed activated upon PRRSV infection, as evidenced by IκB phosphorylation and degradation. Moreover, we revealed an NF-κB binding motif in the cloned porcine IL-15 (pIL-15) promoter, deletion of which abrogated the pIL-15 promoter activity in PRRSV-infected alveolar macrophages. In addition, we demonstrated that PRRSV nucleocapsid (N) protein had the ability to induce IL-15 production in porcine alveolar macrophage cell line CRL2843 by transient transfection, which was mediated by its multiple motifs, and it also activated NF-κB. These data indicated that PRRSV infection-induced IL-15 production was likely through PRRSV N protein-mediated NF-κB activation. Our findings provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms underling the IL-15 production induced by PRRSV infection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection activates IL-10 production through NF-κB and p38 MAPK pathways in porcine alveolar macrophages.Dev Comp Immunol. 2013 Mar;39(3):265-72. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Dev Comp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23085400
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) up-regulates IL-15 through PKCβ1-TAK1-NF-κB signaling pathway.Virology. 2016 Sep;496:166-174. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Virology. 2016. PMID: 27318153
-
Highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (HP-PRRSV) induces IL-6 production through TAK-1/JNK/AP-1 and TAK-1/NF-κB signaling pathways.Vet Microbiol. 2021 May;256:109061. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2021.109061. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Vet Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33836390
-
Coinfection with bacterial pathogens and genetic modification of PRRSV-2 for suppression of NF-κB and attenuation of proinflammatory responses.Virology. 2025 May;606:110484. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2025.110484. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Virology. 2025. PMID: 40086205 Review.
-
Antagonizing interferon-mediated immune response by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:315470. doi: 10.1155/2014/315470. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25101271 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heat stress causes oxidative stress but not inflammatory signaling in porcine skeletal muscle.Temperature (Austin). 2014 Apr 17;1(1):42-50. doi: 10.4161/temp.28844. eCollection 2014 Apr-Jun. Temperature (Austin). 2014. PMID: 27583280 Free PMC article.
-
Highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus induces prostaglandin E2 production through cyclooxygenase 1, which is dependent on the ERK1/2-p-C/EBP-β pathway.J Virol. 2014 Mar;88(5):2810-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03205-13. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24352469 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of interleukin-10 is dependent on p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in macrophages infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.Virol J. 2012 Aug 21;9:165. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-165. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22909062 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus structural protein GP2 in apoptosis inhibition.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:160505. doi: 10.1155/2014/160505. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24511529 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the N protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 29;15:1391697. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1391697. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38741730 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad R, El Bassam S, Cordeiro P, Menezes J. 2008. Requirement of TLR2-mediated signaling for the induction of IL-15 gene expression in human monocytic cells by HSV-1. Blood 112:2360–2368 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad R, Ennaciri J, Cordeiro P, El Bassam S, Menezes J. 2007. Herpes simplex virus-1 up-regulates IL-15 gene expression in monocytic cells through the activation of protein tyrosine kinase and PKC zeta/lambda signaling pathways. J. Mol. Biol. 367:25–35 - PubMed
-
- Ankel H, Westra DF, Welling-Wester S, Lebon P. 1998. Induction of interferon-alpha by glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus: a possible role of chemokine receptors. Virology 251:317–326 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

