A platinum-based covalent viability reagent for single-cell mass cytometry
- PMID: 22577098
- PMCID: PMC3808967
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.22067
A platinum-based covalent viability reagent for single-cell mass cytometry
Abstract
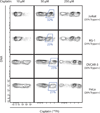
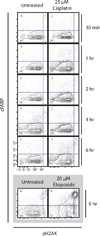
In fluorescence-based flow cytometry, cellular viability is determined with membrane-impermeable fluorescent reagents that specifically enter and label plasma membrane-compromised nonviable cells. A recent technological advance in flow cytometry uses antibodies conjugated to elemental metal isotopes, rather than to fluorophores, to allow signal detection by atomic mass spectrometry. Unhampered by the limitations of overlapping emission fluorescence, mass cytometry increases the number of parameters that can be measured in single cells. However, mass cytometry is unable to take advantage of current fluorescent viability dyes. An alternative methodology was therefore developed here in which the platinum-containing chemotherapy drug cisplatin was used to resolve live and dead cells by mass cytometry. In a 1-min incubation step, cisplatin preferentially labeled nonviable cells from both adherent and suspension cultures, resulting in a platinum signal quantifiable by mass cytometry. This protocol was compatible with established sample processing steps for intracellular cytometry. Furthermore, the live/dead ratios were comparable between mass- and fluorescence-based cytometry. Importantly, although cisplatin is a known DNA-damaging agent, a 1-min "pulse" of cisplatin did not induce observable DNA damage or apoptotic responses even within 6-h post-exposure. Cisplatin can therefore be used as a viability reagent for a wide range of mass cytometry protocols.
Copyright © 2012 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Schmid I, Krall WJ, Uittenbogaart CH, Braun J, Giorgi JV. Dead cell discrimination with 7-amino-actinomycin D in combination with dual color immunofluorescence in single laser flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1992;13:204–208. - PubMed
-
- Moore A, Donahue CJ, Bauer KD, Mather JP. Simultaneous measurement of cell cycle and apoptotic cell death. Methods Cell Biol. 1998;57:265–278. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien MC, Bolton WE. Comparison of cell viability probes compatible with fixation and permeabilization for combined surface and intracellular staining in flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1995;19:243–255. - PubMed
-
- Perfetto SP, Chattopadhyay PK, Lamoreaux L, Nguyen R, Ambrozak D, Koup RA, Roederer M. Amine reactive dyes: an effective tool to discriminate live and dead cells in polychromatic flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 2006;313:199–208. - PubMed
-
- Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F, Riccardi C. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1991;139:271–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA130826/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA143907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA034233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007328/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HV-10-05(2)/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA149145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA130826/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U54CA143907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA149145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 09-011/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000034C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057229/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA119367/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272200700038C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

