Diverse roles of macrophages in atherosclerosis: from inflammatory biology to biomarker discovery
- PMID: 22577254
- PMCID: PMC3337637
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/693083
Diverse roles of macrophages in atherosclerosis: from inflammatory biology to biomarker discovery
Abstract
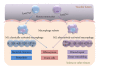
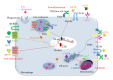
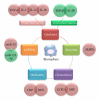
Cardiovascular disease, a leading cause of mortality in developed countries, is mainly caused by atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease. Macrophages, which differentiate from monocytes that are recruited from the blood, account for the majority of leukocytes in atherosclerotic plaques. Apoptosis and the suppressed clearance of apoptotic macrophages (efferocytosis) are associated with vulnerable plaques that are prone to rupture, leading to thrombosis. Based on the central functions of macrophages in atherogenesis, cytokines, chemokines, enzymes, or microRNAs related to or produced by macrophages have become important clinical prognostic or diagnostic biomarkers. This paper discusses the impact of monocyte-derived macrophages in early atherogenesis and advanced disease. The role and possible future development of macrophage inflammatory biomarkers are also described.
Figures


References
-
- Dahlöf B. Cardiovascular disease risk factors: epidemiology and risk assessment. American Journal of Cardiology. 2010;105(1):3A–9A. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM. Cardiovascular risk prediction: basic concepts, current status, and future directions. Circulation. 2010;121(15):1768–1777. - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK. Mechanisms of disease: inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;352(16):1685–1696. - PubMed
-
- Mayerl C, Lukasser M, Sedivy R, Niederegger H, Seiler R, Wick G. Atherosclerosis research from past to present—on the track of two pathologists with opposing views, Carl von Rokitansky and Rudolf Virchow. Virchows Archiv. 2006;449(1):96–103. - PubMed
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 1999;340(2):115–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

