Blood Pressure over Height Ratios: Simple and Accurate Method of Detecting Elevated Blood Pressure in Children
- PMID: 22577400
- PMCID: PMC3332207
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/253497
Blood Pressure over Height Ratios: Simple and Accurate Method of Detecting Elevated Blood Pressure in Children
Abstract
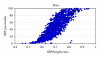
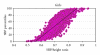
Background. Blood pressure (BP) percentiles in childhood are assessed according to age, gender, and height. Objective. To create a simple BP/height ratio for both systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP). To study the relationship between BP/height ratios and corresponding BP percentiles in children. Methods. We analyzed data on height and BP from 2006-2007 NHANES data. BP percentiles were calculated for 3775 children. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were performed to calculate sensitivity and specificity of BP/height ratios as diagnostic tests for elevated BP (>90%). Correlation analysis was performed between BP percentiles and BP/height ratios. Results. The average age was 12.54 ± 2.67 years. SBP/height and DBP/height ratios strongly correlated with SBP & DBP percentiles in both boys (P < 0.001, R(2) = 0.85, R(2) = 0.86) and girls (P < 0.001, R(2) = 0.85, R(2) = 0.90). The cutoffs of SBP/height and DBP/height ratios in boys were ≥0.75 and ≥0.46, respectively; in girls the ratios were ≥0.75 and ≥0.48, respectively with sensitivity and specificity in range of 83-100%. Conclusion. BP/height ratios are simple with high sensitivity and specificity to detect elevated BP in children. These ratios can be easily used in routine medical care of children.
Figures
References
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42(6):1206–1252. - PubMed
-
- Falkner B, Daniels SR, Flynn JT, et al. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2004;114(supplement 2):555–576. - PubMed
-
- Sorof JM, Lai D, Turner J, Poffenbarger T, Portman RJ. Overweight, ethnicity, and the prevalence of hypertension in school-aged children. Pediatrics. 2004;113(3, part 1):475–482. - PubMed
-
- Sorof J, Daniels S. Obesity hypertension in children: a problem of epidemic proportions. Hypertension. 2002;40(4):441–447. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999-2000. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2002;288(14):1728–1732. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

