Structural basis for calmodulin as a dynamic calcium sensor
- PMID: 22579256
- PMCID: PMC3372094
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2012.03.019
Structural basis for calmodulin as a dynamic calcium sensor
Abstract
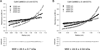
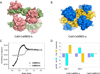
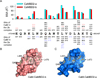
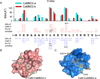
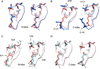
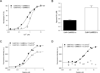
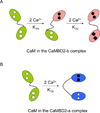
Calmodulin is a prototypical and versatile Ca(2+) sensor with EF hands as its high-affinity Ca(2+) binding domains. Calmodulin is present in all eukaryotic cells, mediating Ca(2+)-dependent signaling. Upon binding Ca(2+), calmodulin changes its conformation to form complexes with a diverse array of target proteins. Despite a wealth of knowledge on calmodulin, little is known on how target proteins regulate calmodulin's ability to bind Ca(2+). Here, we take advantage of two splice variants of SK2 channels, which are activated by Ca(2+)-bound calmodulin but show different sensitivity to Ca(2+) for their activation. Protein crystal structures and other experiments show that, depending on which SK2 splice variant it binds to, calmodulin adopts drastically different conformations with different affinities for Ca(2+) at its C-lobe. Such target protein-induced conformational changes make calmodulin a dynamic Ca(2+) sensor capable of responding to different Ca(2+) concentrations in cellular Ca(2+) signaling.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interests for the authors involved in this work.
Figures




References
-
- Andersson A, Forsén S, Thulin E, HJ V. Cadmium-113 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of proteolytic fragments of calmodulin: assignment of strong and weak cation binding sites. Biochem. 1983;22:2309–2313. - PubMed
-
- Bond CT, Maylie J, Adelman JP. SK channels in excitability, pacemaking and synaptic integration. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2005;15:305–311. - PubMed
-
- Chin D, Means AR. Calmodulin: a prototypical calcium sensor. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10:322–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

