CB₂ cannabinoid receptors inhibit synaptic transmission when expressed in cultured autaptic neurons
- PMID: 22579668
- PMCID: PMC3392362
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.04.024
CB₂ cannabinoid receptors inhibit synaptic transmission when expressed in cultured autaptic neurons
Abstract
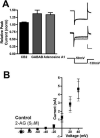
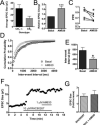
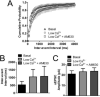
The role of CB₂ in the central nervous system, particularly in neurons, has generated much controversy. Fueling the controversy are imperfect tools, which have made conclusive identification of CB₂ expressing neurons problematic. Imprecise localization of CB₂ has made it difficult to determine its function in neurons. Here we avoid the localization controversy and directly address the question if CB₂ can modulate neurotransmission. CB₂ was expressed in excitatory hippocampal autaptic neurons obtained from CB₁ null mice. Whole-cell patch clamp recordings were made from these neurons to determine the effects of CB₂ on short-term synaptic plasticity. CB₂ expression restored depolarization induced suppression of excitation to these neurons, which was lost following genetic ablation of CB₁. The endocannabinoid 2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG) mimicked the effects of depolarization in CB₂ expressing neurons. Interestingly, ongoing basal production of 2-AG resulted in constitutive activation of CB₂, causing a tonic inhibition of neurotransmission that was relieved by the CB₂ antagonist AM630 or the diacylglycerol lipase inhibitor RHC80267. Through immunocytochemistry and analysis of spontaneous EPSCs, paired pulse ratios and coefficients of variation we determined that CB₂ exerts its function at a presynaptic site of action, likely through inhibition of voltage gated calcium channels. Therefore CB₂ expressed in neurons effectively mimics the actions of CB₁. Thus neuronal CB₂ is well suited to integrate into conventional neuronal endocannabinoid signaling processes, with its specific role determined by its unique and highly inducible expression profile.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
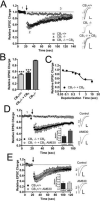
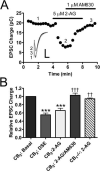

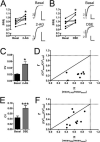
References
-
- Ashton JC, Rahman RM, Nair SM, Sutherland BA, Glass M, Appleton I. Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia and middle cerebral artery occlusion induce expression of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in the brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2007;412:114–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

