The biological kinship of hypoxia with CSC and EMT and their relationship with deregulated expression of miRNAs and tumor aggressiveness
- PMID: 22579961
- PMCID: PMC3788359
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.04.008
The biological kinship of hypoxia with CSC and EMT and their relationship with deregulated expression of miRNAs and tumor aggressiveness
Abstract
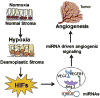
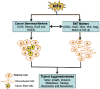
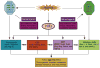
Hypoxia is one of the fundamental biological phenomena that are intricately associated with the development and aggressiveness of a variety of solid tumors. Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) function as a master transcription factor, which regulates hypoxia responsive genes and has been recognized to play critical roles in tumor invasion, metastasis, and chemo-radiation resistance, and contributes to increased cell proliferation, survival, angiogenesis and metastasis. Therefore, tumor hypoxia with deregulated expression of HIF and its biological consequence lead to poor prognosis of patients diagnosed with solid tumors, resulting in higher mortality, suggesting that understanding of the molecular relationship of hypoxia with other cellular features of tumor aggressiveness would be invaluable for developing newer targeted therapy for solid tumors. It has been well recognized that cancer stem cells (CSCs) and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenotypic cells are associated with therapeutic resistance and contribute to aggressive tumor growth, invasion, metastasis and believed to be the cause of tumor recurrence. Interestingly, hypoxia and HIF signaling pathway are known to play an important role in the regulation and sustenance of CSCs and EMT phenotype. However, the molecular relationship between HIF signaling pathway with the biology of CSCs and EMT remains unclear although NF-κB, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Notch, Wnt/β-catenin, and Hedgehog signaling pathways have been recognized as important regulators of CSCs and EMT. In this article, we will discuss the state of our knowledge on the role of HIF-hypoxia signaling pathway and its kinship with CSCs and EMT within the tumor microenvironment. We will also discuss the potential role of hypoxia-induced microRNAs (miRNAs) in tumor development and aggressiveness, and finally discuss the potential effects of nutraceuticals on the biology of CSCs and EMT in the context of tumor hypoxia.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Fyles A, Milosevic M, Hedley D, Pintilie M, Levin W, Manchul L, Hill RP. Tumor hypoxia has independent predictor impact only in patients with node-negative cervix cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:680–687. - PubMed
-
- Hockel M, Schlenger K, Aral B, Mitze M, Schaffer U, Vaupel P. Association between tumor hypoxia and malignant progression in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix. Cancer Res. 1996;56:4509–4515. - PubMed
-
- Moulder JE, Rockwell S. Tumor hypoxia: its impact on cancer therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1987;5:313–341. - PubMed
-
- Teicher BA. Hypoxia and drug resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1994;13:139–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

