Regulation of E2F1 by APC/C Cdh1 via K11 linkage-specific ubiquitin chain formation
- PMID: 22580462
- PMCID: PMC3359126
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.20643
Regulation of E2F1 by APC/C Cdh1 via K11 linkage-specific ubiquitin chain formation
Abstract
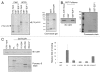
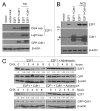
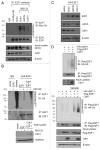
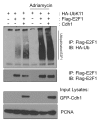
E2F1 is a eukaryotic transcription factor that is known to regulate various cellular pathways such as cell cycle progression, DNA replication, DNA damage responses and induction of apoptosis. Given its versatile roles, a precise and tight regulation of E2F1 is very critical to maintain genomic stability. E2F1 is regulated both at transcriptional and posttranslational levels during cell cycle and upon DNA damage. After S phase, E2F1 is targeted for degradation and is kept at low levels or in an inactive state until the next G 1/S phase transition. Our studies show that APC/C ubiquitin ligase in conjunction with its co-activator Cdh1 (APC/C (Cdh1) ) can downregulate E2F1. We also identify an APC/C subunit APC5 that binds to E2F1 and is essential for E2F1 ubiquitination. We confirm an interaction between E2F1 and Cdh1 as well as an interaction between E2F1 and APC5 both in vivo and in vitro. In vitro GST pull-down assays have mapped the C-terminal 79 a.a. of E2F1 as Cdh1 interacting residues. Ectopically expressed Cdh1 downregulates the expression of E2F1-4. Our studies have also shown for the first time that E2F1 can be modified by K11-linkage specific ubiquitin chain formation (Ub-K11). The formation of Ub-K11 chains on E2F1 is increased in the presence of Cdh1 and accumulated in the presence of proteasome inhibitor, suggesting that APC/C (Cdh1) targets E2F1 for degradation by forming Ub-K11 chains. We also show that the effect of Cdh1 on E2F1 degradation is blocked upon DNA damage. Interestingly, Ub-K11-linked E2F1 accumulates after treatment of DNA damaging agents. The data suggest that DNA damage signaling processes do not inhibit APC/C (Cdh1) to ubiquitinate E2F1. Instead, they block the proteasomal degradation of Ub-K11-linked E2F1, and therefore lead to its accumulation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
APC/C(Cdc20) targets E2F1 for degradation in prometaphase.Cell Cycle. 2010 Oct 1;9(19):3956-64. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.19.13162. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20948288 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation and disassembly of the anaphase-promoting complex during human cytomegalovirus infection is associated with degradation of the APC5 and APC4 subunits and does not require UL97-mediated phosphorylation of Cdh1.J Virol. 2010 Oct;84(20):10832-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01260-10. Epub 2010 Aug 4. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20686030 Free PMC article.
-
Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome participates in the acute response to protein-damaging stress.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;30(24):5608-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01506-09. Epub 2010 Oct 11. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20937767 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of APC/CCdh1 in development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Aug;22(6):579-85. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.03.012. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21497201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-mitotic functions of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Aug;22(6):572-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.03.010. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21439391 Review.
Cited by
-
Flipping the switch from g1 to s phase with e3 ubiquitin ligases.Genes Cancer. 2012 Nov;3(11-12):634-48. doi: 10.1177/1947601912473307. Genes Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23634252 Free PMC article.
-
DLGAP5 triggers proliferation and metastasis of bladder cancer by stabilizing E2F1 via USP11.Oncogene. 2024 Feb;43(8):594-607. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02932-y. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38182895
-
Feedback regulation between atypical E2Fs and APC/CCdh1 coordinates cell cycle progression.EMBO Rep. 2016 Mar;17(3):414-27. doi: 10.15252/embr.201540984. Epub 2016 Feb 5. EMBO Rep. 2016. PMID: 26882548 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitination Links DNA Damage and Repair Signaling to Cancer Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 8;24(9):8441. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098441. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRR11 promotes ccRCC tumorigenesis by regulating E2F1 stability.JCI Insight. 2021 Oct 8;6(19):e145172. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.145172. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34499617 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeGregori J, Johnson DG. Distinct and Overlapping Roles for E2F Family Members in Transcription, Proliferation and Apoptosis. Curr Mol Med. 2006;6:739–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
