Sororin is a master regulator of sister chromatid cohesion and separation
- PMID: 22580470
- PMCID: PMC3368859
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.20241
Sororin is a master regulator of sister chromatid cohesion and separation
Abstract
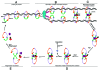
The maintenance of sister chromatid cohesion from S phase to the onset of anaphase relies on a small but evolutionarily conserved protein called Sororin. Sororin is a phosphoprotein and its dynamic localization and function are regulated by protein kinases, such as Cdk1/cyclin B and Erk2. The association of Sororin with chromatin requires cohesin to be preloaded to chromatin and modification of Smc3 during DNA replication. Sororin antagonizes the function of Wapl in cohesin releasing from S to G 2 phase and promotes cohesin release from sister chromatid arms in prophase via interaction with Plk1. This review focuses on progress of the identification and regulation of Sororin during cell cycle; role of post-translational modification on Sororin function; role of Sororin in the maintenance and resolution of sister chromatid cohesion; and finally discusses Sororin's emerging role in cancer and the potential issues that need be addressed in the future.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aurora B and Cdk1 mediate Wapl activation and release of acetylated cohesin from chromosomes by phosphorylating Sororin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 13;110(33):13404-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305020110. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23901111 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Sororin protein with polo-like kinase 1 mediates resolution of chromosomal arm cohesion.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 2;286(48):41826-41837. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.305888. Epub 2011 Oct 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21987589 Free PMC article.
-
Sororin is required for stable binding of cohesin to chromatin and for sister chromatid cohesion in interphase.Curr Biol. 2007 Apr 3;17(7):630-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.02.029. Epub 2007 Mar 8. Curr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17349791
-
Sister chromatid cohesion.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Nov 1;4(11):a011130. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a011130. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 23043155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expanding phenotypes of cohesinopathies: one ring to rule them all!Cell Cycle. 2019 Nov;18(21):2828-2848. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1658476. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 31516082 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sororin is tethered to Cohesin SA2.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(8):1133. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1018055. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25695517 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Discovery and Validation of a Compound to Target Ewing's Sarcoma.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 24;13(10):1553. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13101553. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34683845 Free PMC article.
-
CDCA5 promotes the progression of breast cancer and serves as a potential prognostic biomarker.Oncol Rep. 2022 Oct;48(4):172. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8387. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36004470 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing alterations contributing to cancer hallmarks in the liver: central role of dedifferentiation and genome instability.Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Oct 31;3:84. doi: 10.21037/tgh.2018.10.11. eCollection 2018. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30505971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Comprehensive Analysis Illustrates the Role of CDCA5 in Breast Cancer: An Effective Diagnosis and Prognosis Biomarker.Int J Genomics. 2023 May 30;2023:7150141. doi: 10.1155/2023/7150141. eCollection 2023. Int J Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37287817 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
