The KDEL receptor couples to Gαq/11 to activate Src kinases and regulate transport through the Golgi
- PMID: 22580821
- PMCID: PMC3395092
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.134
The KDEL receptor couples to Gαq/11 to activate Src kinases and regulate transport through the Golgi
Abstract
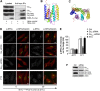
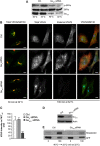
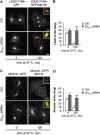
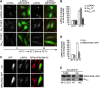
Membrane trafficking involves large fluxes of cargo and membrane across separate compartments. These fluxes must be regulated by control systems to maintain homoeostasis. While control systems for other key functions such as protein folding or the cell cycle are well known, the mechanisms that control secretory transport are poorly understood. We have previously described a signalling circuit operating at the Golgi complex that regulates intra-Golgi trafficking and is initiated by the KDEL receptor (KDEL-R), a protein previously known to mediate protein recycling from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Here, we investigated the KDEL-R signalling mechanism. We show that the KDEL-R is predicted to fold like a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), and that it binds and activates the heterotrimeric signalling G-protein Gα(q/11) which, in turn, regulates transport through the Golgi complex. These findings reveal an unexpected GPCR-like mode of action of the KDEL-R and shed light on a core molecular control mechanism of intra-Golgi traffic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
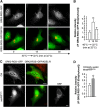
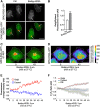
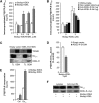
References
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts KPW (2002) Molecular Biology of the Cell 4th ednNew York: Garland Science
-
- Balch WE, Dunphy WG, Braell WA, Rothman JE (1984) Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell 39: 2 Part 1405–416 - PubMed
-
- Berman DM, Kozasa T, Gilman AG (1996) The GTPase-activating protein RGS4 stabilizes the transition state for nucleotide hydrolysis. J Biol Chem 271: 27209–27212 - PubMed
-
- Bonazzi M, Spano S, Turacchio G, Cericola C, Valente C, Colanzi A, Kweon HS, Hsu VW, Polishchuck EV, Polishchuck RS, Sallese M, Pulvirenti T, Corda D, Luini A (2005) CtBP3/BARS drives membrane fission in dynamin-independent transport pathways. Nat Cell Biol 7: 570–580 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

