DOCK8 functions as an adaptor that links TLR-MyD88 signaling to B cell activation
- PMID: 22581261
- PMCID: PMC3362684
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2305
DOCK8 functions as an adaptor that links TLR-MyD88 signaling to B cell activation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: DOCK8 functions as an adaptor that links TLR-MyD88 signaling to B cell activation.Nat Immunol. 2022 May;23(5):815. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01180-8. Nat Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35332329 No abstract available.
Abstract
The adaptors DOCK8 and MyD88 have been linked to serological memory. Here we report that DOCK8-deficient patients had impaired antibody responses and considerably fewer CD27(+) memory B cells. B cell proliferation and immunoglobulin production driven by Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) were considerably lower in DOCK8-deficient B cells, but those driven by the costimulatory molecule CD40 were not. In contrast, TLR9-driven expression of AICDA (which encodes the cytidine deaminase AID), the immunoglobulin receptor CD23 and the costimulatory molecule CD86 and activation of the transcription factor NF-κB, the kinase p38 and the GTPase Rac1 were intact. DOCK8 associated constitutively with MyD88 and the tyrosine kinase Pyk2 in normal B cells. After ligation of TLR9, DOCK8 became tyrosine-phosphorylated by Pyk2, bound the Src-family kinase Lyn and linked TLR9 to a Src-kinase Syk-transcription factor STAT3 cascade essential for TLR9-driven B cell proliferation and differentiation. Thus, DOCK8 functions as an adaptor in a TLR9-MyD88 signaling pathway in B cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
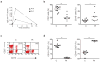

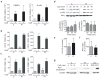

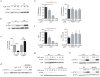

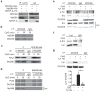
References
-
- Yoshida T, et al. Memory B and memory plasma cells. Immunol Rev. 2010;237:117–139. - PubMed
-
- Jiang W, et al. TLR9 stimulation drives naive B cells to proliferate and to attain enhanced antigen presenting function. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:2205–2213. - PubMed
-
- Giordani L, et al. IFN-alpha amplifies human naive B cell TLR-9-mediated activation and Ig production. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86:261–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32AI007512/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI076625/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AI094017/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007512/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI080002/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI100315/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01AI076210/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI065617/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21AI087627/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI076210/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08AI076625/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI087627/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI083503/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI083503/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

