Identification of novel NRF2-regulated genes by ChIP-Seq: influence on retinoid X receptor alpha
- PMID: 22581777
- PMCID: PMC3424561
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks409
Identification of novel NRF2-regulated genes by ChIP-Seq: influence on retinoid X receptor alpha
Abstract
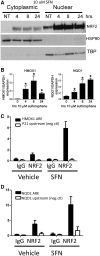
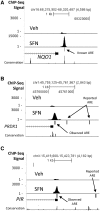
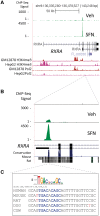
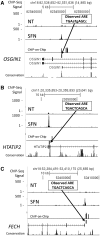
Cellular oxidative and electrophilic stress triggers a protective response in mammals regulated by NRF2 (nuclear factor (erythroid-derived) 2-like; NFE2L2) binding to deoxyribonucleic acid-regulatory sequences near stress-responsive genes. Studies using Nrf2-deficient mice suggest that hundreds of genes may be regulated by NRF2. To identify human NRF2-regulated genes, we conducted chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-sequencing experiments in lymphoid cells treated with the dietary isothiocyanate, sulforaphane (SFN) and carried out follow-up biological experiments on candidates. We found 242 high confidence, NRF2-bound genomic regions and 96% of these regions contained NRF2-regulatory sequence motifs. The majority of binding sites were near potential novel members of the NRF2 pathway. Validation of selected candidate genes using parallel ChIP techniques and in NRF2-silenced cell lines indicated that the expression of about two-thirds of the candidates are likely to be directly NRF2-dependent including retinoid X receptor alpha (RXRA). NRF2 regulation of RXRA has implications for response to retinoid treatments and adipogenesis. In mouse, 3T3-L1 cells' SFN treatment affected Rxra expression early in adipogenesis, and knockdown of Nrf2-delayed Rxra expression, both leading to impaired adipogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel hematopoietic target genes in the NRF2-mediated transcriptional pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:120305. doi: 10.1155/2013/120305. Epub 2013 May 25. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 23766848 Free PMC article.
-
PFOS induces adipogenesis and glucose uptake in association with activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Jan 1;290:21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.11.002. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26548598 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane reactivates cellular antioxidant defense by inducing Nrf2/ARE/Prdx6 activity during aging and oxidative stress.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 26;7(1):14130. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14520-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29074861 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Nrf2- and AP-1-mediated gene expression by epigallocatechin-3-gallate and sulforaphane in prostate of Nrf2-knockout or C57BL/6J mice and PC-3 AP-1 human prostate cancer cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Sep;31(9):1223-40. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.147. Epub 2010 Aug 23. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010. PMID: 20729872 Free PMC article.
-
The phytoprotective agent sulforaphane prevents inflammatory degenerative diseases and age-related pathologies via Nrf2-mediated hormesis.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jan;163:105283. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105283. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33160067 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress responses and NRF2 in human leukaemia.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:454659. doi: 10.1155/2015/454659. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 25918581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2 regulates PU.1 expression and activity in the alveolar macrophage.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 May 15;308(10):L1086-93. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00355.2014. Epub 2015 Apr 3. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25840997 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of the anti-ageing effects of polyphenolics: mitigation of oxidative stress.BMC Chem. 2020 Aug 10;14(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13065-020-00696-0. eCollection 2020 Dec. BMC Chem. 2020. PMID: 32793891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between microRNAs and Nrf2 signaling in human cancers.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Jul 5;24(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03430-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38970040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcription factor, Nuclear factor, erythroid 2 (Nfe2), is a regulator of the oxidative stress response during Danio rerio development.Aquat Toxicol. 2016 Nov;180:141-154. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.09.019. Epub 2016 Oct 1. Aquat Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27716579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Katoh Y, Oyake T, Hayashi N, Satoh K, Hatayama I, et al. An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997;236:313–322. - PubMed
-
- Hayes JD, McMahon M. Molecular basis for the contribution of the antioxidant responsive element to cancer chemoprevention. Cancer. Lett. 2001;174:103–113. - PubMed
-
- Rushmore TH, Morton MR, Pickett CB. The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:11632–11639. - PubMed
-
- Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S. Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007;47:89–116. - PubMed
-
- Lee JM, Calkins MJ, Chan K, Kan YW, Johnson JA. Identification of the NF-E2-related factor-2-dependent genes conferring protection against oxidative stress in primary cortical astrocytes using oligonucleotide microarray analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:12029–12038. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

