Biochemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology of NADPH oxidases in the cardiovascular system
- PMID: 22581922
- PMCID: PMC3365576
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.243972
Biochemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology of NADPH oxidases in the cardiovascular system
Abstract
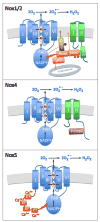
The NADPH oxidase (Nox) enzymes are critical mediators of cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. These proteins are expressed in virtually all cardiovascular cells, and regulate such diverse functions as differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, senescence, inflammatory responses and oxygen sensing. They target a number of important signaling molecules, including kinases, phosphatases, transcription factors, ion channels, and proteins that regulate the cytoskeleton. Nox enzymes have been implicated in many different cardiovascular pathologies: atherosclerosis, hypertension, cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling, angiogenesis and collateral formation, stroke, and heart failure. In this review, we discuss in detail the biochemistry of Nox enzymes expressed in the cardiovascular system (Nox1, 2, 4, and 5), their roles in cardiovascular cell biology, and their contributions to disease development.
Figures
References
-
- Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX family of ros-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiological reviews. 2007;87:245–313. - PubMed
-
- Bayraktutan U, Blayney L, Shah AM. Molecular characterization and localization of the NAD(P)H oxidase components gp91-phox and p22-phox in endothelial cells. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2000;20:1903–1911. - PubMed
-
- Hohler B, Holzapfel B, Kummer W. NADPH oxidase subunits and superoxide production in porcine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Histochemistry and cell biology. 2000;114:29–37. - PubMed
-
- Lassegue B, Clempus RE. Vascular NAD(P)H oxidases: Specific features, expression, and regulation. American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology. 2003;285:R277–297. - PubMed
-
- Sumimoto H. Structure, regulation and evolution of nox-family NADPH oxidases that produce reactive oxygen species. The FEBS journal. 2008;275:3249–3277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

