Osteopontin is an endogenous modulator of the constitutively activated phenotype of pulmonary adventitial fibroblasts in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 22582113
- PMCID: PMC3426432
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00050.2012
Osteopontin is an endogenous modulator of the constitutively activated phenotype of pulmonary adventitial fibroblasts in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
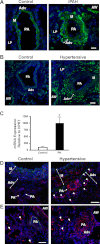
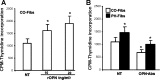
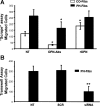
Increased cell proliferation and migration, of several cell types are key components of vascular remodeling observed in pulmonary hypertension (PH). Our previous data demonstrate that adventitial fibroblasts isolated from pulmonary arteries of chronically hypoxic hypertensive calves (termed PH-Fibs) exhibit a "constitutively activated" phenotype characterized by high proliferative and migratory potential. Osteopontin (OPN) has been shown to promote several cellular activities including growth and migration in cancer cells. We thus tested the hypothesis that elevated OPN expression confers the "activated" highly proproliferative and promigratory/invasive phenotype of PH-Fibs. Our results demonstrate that, both in vivo and ex vivo, PH-Fibs exhibited increased expression of OPN, as well as its cognate receptors, α(V)β(3) and CD44, compared with control fibroblasts (CO-Fibs). Augmented OPN expression in PH-Fibs corresponded to their high proliferative, migratory, and invasive properties and constitutive activation of ERK1/2 and AKT signaling. OPN silencing via small interfering RNA or sequestering OPN production by specific antibodies led to decreased proliferation, migration, invasion, and attenuated ERK1/2, AKT phosphorylation in PH-Fibs. Furthermore, increasing OPN levels in CO-Fibs via recombinant OPN resulted in significant increases in their proliferative, migratory, and invasive capabilities to the levels resembling those of PH-Fibs. Thus our data suggest OPN as an essential contributor to the activated (highly proliferative, migratory, and proinvasive) phenotype of pulmonary adventitial fibroblasts in hypoxic PH.
Figures


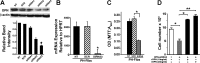

References
-
- Angelucci A, Festuccia C, Gravina GL, Muzi P, Bonghi L, Vicentini C, Bologna M. Osteopontin enhances the cell proliferation induced by the epidermal growth factor in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate 59: 157–166, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Anwar A, Dehn D, Siegel D, Kepa JK, Tang LJ, Pietenpol JA, Ross D. Interaction of human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) with the tumor suppressor protein p53 in cells and cell-free systems. J Biol Chem 278: 10368–10373, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Archer S, Rich S. Primary pulmonary hypertension: a vascular biology and translational research “Work in progress”. Circulation 102: 2781–2791, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

