Recent explosive human population growth has resulted in an excess of rare genetic variants
- PMID: 22582263
- PMCID: PMC3586590
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1217283
Recent explosive human population growth has resulted in an excess of rare genetic variants
Abstract
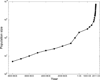
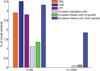
Human populations have experienced recent explosive growth, expanding by at least three orders of magnitude over the past 400 generations. This departure from equilibrium skews patterns of genetic variation and distorts basic principles of population genetics. We characterized the empirical signatures of explosive growth on the site frequency spectrum and found that the discrepancy in rare variant abundance across demographic modeling studies is mostly due to differences in sample size. Rapid recent growth increases the load of rare variants and is likely to play a role in the individual genetic burden of complex disease risk. Hence, the extreme recent human population growth needs to be taken into consideration in studying the genetics of complex diseases and traits.
Figures

References
-
- Cohen JE. How Many People Can the Earth Support? ed. 1. New York: Norton; 1995.
-
- Roberts L. Science. 2011;333:540. - PubMed
-
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division. 2011
-
- Hartl D, Clark A. Principles of Population Genetics. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer; 2007.
-
- Gravel S, et al. 1000 Genomes Project. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011;108:11983.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

