The MEKK1 SWIM domain is a novel substrate receptor for c-Jun ubiquitylation
- PMID: 22582703
- PMCID: PMC3653270
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20120406
The MEKK1 SWIM domain is a novel substrate receptor for c-Jun ubiquitylation
Abstract
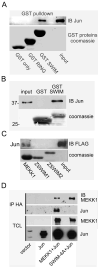
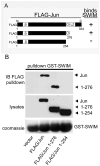
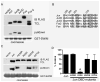
MEKK1 [MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase)/ERK (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase) kinase kinase 1] is a MAP3K (MAPK kinase kinase) that regulates MAPK activation, and is the only known mammalian kinase that is also a ubiquitin ligase. MEKK1 contains a RING domain within its N-terminal regulatory region, and MEKK1 has been shown to ubiquitylate the AP-1 (activator protein 1) transcription factor protein c-Jun, but the mechanism by which MEKK1 interacts with c-Jun to induce ubiquitylation has not been defined. Proximal to the RING domain is a SWIM (SWI2/SNF2 and MuDR) domain of undetermined function. In the present study, we demonstrate that the MEKK1 SWIM domain, but not the RING domain, directly associates with the c-Jun DNA-binding domain, and that the SWIM domain is required for MEKK1-dependent c-Jun ubiquitylation. We further show that this MEKK1 SWIM-Jun interaction is specific, as SWIM domains from other proteins failed to bind c-Jun. We reveal that, although the Jun and Fos DNA-binding domains are highly conserved, the MEKK1 SWIM domain does not bind Fos. Finally, we identify the sequence unique to Jun proteins required for specific interaction with the MEKK1 SWIM domain. Therefore we propose that the MEKK1 SWIM domain represents a novel substrate-binding domain necessary for direct interaction between c-Jun and MEKK1 that promotes MEKK1-dependent c-Jun ubiquitylation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High yield purification of JNK1β1 and activation by in vitro reconstitution of the MEKK1→MKK4→JNK MAPK phosphorylation cascade.Protein Expr Purif. 2013 Feb;87(2):87-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2012.10.010. Epub 2012 Nov 10. Protein Expr Purif. 2013. PMID: 23147205
-
JSAP1, a novel jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK)-binding protein that functions as a Scaffold factor in the JNK signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Nov;19(11):7539-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.11.7539. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10523642 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress inhibits MEKK1 by site-specific glutathionylation in the ATP-binding domain.Biochem J. 2004 Aug 1;381(Pt 3):675-83. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040591. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15139849 Free PMC article.
-
Wiring diagrams of MAPK regulation by MEKK1, 2, and 3.Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Dec;82(6):658-63. doi: 10.1139/o04-114. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15674433 Review.
-
Genetic Control of MAP3K1 in Eye Development and Sex Differentiation.Cells. 2021 Dec 23;11(1):34. doi: 10.3390/cells11010034. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011600 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A RING to rule them all? Insights into the Map3k1 PHD motif provide a new mechanistic understanding into the diverse roles of Map3k1.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Apr;22(4):540-8. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.239. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25613373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Frontonasal Dysplasia: Towards an Understanding of Molecular and Developmental Aetiology.Mol Syndromol. 2016 Nov;7(6):312-321. doi: 10.1159/000450533. Epub 2016 Oct 29. Mol Syndromol. 2016. PMID: 27920634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An evolutionarily conserved C4HC3-type E3 ligase regulates plant broad-spectrum resistance against pathogens.Plant Cell. 2022 Apr 26;34(5):1822-1843. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koac055. Plant Cell. 2022. PMID: 35171277 Free PMC article.
-
[TRIM21 Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Interacting with ZSWIM1].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024 May 20;27(5):337-344. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2024.101.13. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38880921 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
MEKK1 Regulates Chemokine Expression in Mammary Fibroblasts: Implications for the Breast Tumor Microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 18;11:609918. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.609918. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33868996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Varshavsky A. Regulated protein degradation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:283–286. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg AL. Functions of the proteasome: from protein degradation and immune surveillance to cancer therapy. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35:12–17. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz AL, Ciechanover A. Targeting proteins for destruction by the ubiquitin system: implications for human pathobiology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2009;49:73–96. - PubMed
-
- Shaulian E, Karin M. AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:E131–136. - PubMed
-
- Shaulian E, Karin M. AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene. 2001;20:2390–2400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

