Cathepsin H functions as an aminopeptidase in secretory vesicles for production of enkephalin and galanin peptide neurotransmitters
- PMID: 22582844
- PMCID: PMC3417130
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07788.x
Cathepsin H functions as an aminopeptidase in secretory vesicles for production of enkephalin and galanin peptide neurotransmitters
Abstract
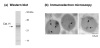
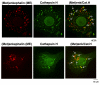
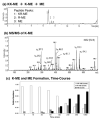
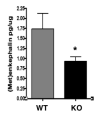
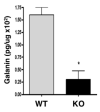
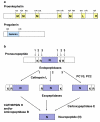
Peptide neurotransmitters function as key intercellular signaling molecules in the nervous system. These peptides are generated in secretory vesicles from proneuropeptides by proteolytic processing at dibasic residues, followed by removal of N- and/or C-terminal basic residues to form active peptides. Enkephalin biosynthesis from proenkephalin utilizes the cysteine protease cathepsin L and the subtilisin-like prohormone convertase 2 (PC2). Cathepsin L generates peptide intermediates with N-terminal basic residue extensions, which must be removed by an aminopeptidase. In this study, we identified cathepsin H as an aminopeptidase in secretory vesicles that produces (Met)enkephalin (ME) by sequential removal of basic residues from KR-ME and KK-ME, supported by in vivo knockout of the cathepsin H gene. Localization of cathepsin H in secretory vesicles was demonstrated by immunoelectron microscopy and immunofluorescence deconvolution microscopy. Purified human cathepsin H sequentially removes N-terminal basic residues to generate ME, with peptide products characterized by nano-LC-MS/MS tandem mass spectrometry. Cathepsin H shows highest activities for cleaving N-terminal basic residues (Arg and Lys) among amino acid fluorogenic substrates. Notably, knockout of the cathepsin H gene results in reduction of ME in mouse brain. Cathepsin H deficient mice also show a substantial decrease in galanin peptide neurotransmitter levels in brain. These results illustrate a role for cathepsin H as an aminopeptidase for enkephalin and galanin peptide neurotransmitter production.
© 2012 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry © 2012 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cathepsin L in secretory vesicles functions as a prohormone-processing enzyme for production of the enkephalin peptide neurotransmitter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Aug 5;100(16):9590-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1531542100. Epub 2003 Jul 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12869695 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin L participates in the production of neuropeptide Y in secretory vesicles, demonstrated by protease gene knockout and expression.J Neurochem. 2008 Jul;106(1):384-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05408.x. Epub 2008 Jul 1. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18410501 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory vesicle aminopeptidase B related to neuropeptide processing: molecular identification and subcellular localization to enkephalin- and NPY-containing chromaffin granules.J Neurochem. 2007 Mar;100(5):1340-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04325.x. Epub 2007 Jan 11. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17241125
-
Cathepsin L and Arg/Lys aminopeptidase: a distinct prohormone processing pathway for the biosynthesis of peptide neurotransmitters and hormones.Biol Chem. 2004 Jun;385(6):473-80. doi: 10.1515/BC.2004.055. Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15255178 Review.
-
Unique biological function of cathepsin L in secretory vesicles for biosynthesis of neuropeptides.Neuropeptides. 2010 Dec;44(6):457-66. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2010.08.003. Epub 2010 Nov 2. Neuropeptides. 2010. PMID: 21047684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cysteine cathepsins in neurological disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Apr;49(2):1017-30. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8576-6. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24234234 Review.
-
A Comprehensive Analysis of Fibromyalgia and the Role of the Endogenous Opioid System.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 11;13(1):165. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010165. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic insights into serum cathepsins as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in knee and hip osteoarthritis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 30;14(1):17553. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68718-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39080459 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the Role of Cysteine Cathepsins in Neuroinflammation.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 30;11(12):1796. doi: 10.3390/biom11121796. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enkephalins and Pain Modulation: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Perspectives.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 30;14(8):926. doi: 10.3390/biom14080926. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brguljan PM, Turk V, Nina C, Brzin J, Krizaj I, Popovic T. Human brain cathepsin H as a neuropeptide and bradykinin metabolizing enzyme. Peptides. 2003;24:1977–1984. - PubMed
-
- Foulon T, Cadel S, Piesse C, Cohen P. Aminopeptidase B. In: Barrett AJ, Rawlings ND, Woessner JF, editors. Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes. 2nd edition 2004. pp. 328–330.
-
- Fricker LD. Carboxypeptidase E. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1988;50:309–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

