3DMolNavi: a web-based retrieval and navigation tool for flexible molecular shape comparison
- PMID: 22583488
- PMCID: PMC3430558
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-95
3DMolNavi: a web-based retrieval and navigation tool for flexible molecular shape comparison
Abstract
Background: Many molecules of interest are flexible and undergo significant shape deformation as part of their function, but most existing methods of molecular shape comparison treat them as rigid shapes, which may lead to incorrect measure of the shape similarity of flexible molecules. Currently, there still is a limited effort in retrieval and navigation for flexible molecular shape comparison, which would improve data retrieval by helping users locate the desirable molecule in a convenient way.
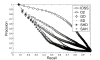
Results: To address this issue, we develop a web-based retrieval and navigation tool, named 3DMolNavi, for flexible molecular shape comparison. This tool is based on the histogram of Inner Distance Shape Signature (IDSS) for fast retrieving molecules that are similar to a query molecule, and uses dimensionality reduction to navigate the retrieved results in 2D and 3D spaces. We tested 3DMolNavi in the Database of Macromolecular Movements (MolMovDB) and CATH. Compared to other shape descriptors, it achieves good performance and retrieval results for different classes of flexible molecules.
Conclusions: The advantages of 3DMolNavi, over other existing softwares, are to integrate retrieval for flexible molecular shape comparison and enhance navigation for user's interaction. 3DMolNavi can be accessed via https://engineering.purdue.edu/PRECISE/3dmolnavi/index.html.
Figures


Similar articles
-
IDSS: deformation invariant signatures for molecular shape comparison.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 May 22;10:157. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-157. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19463181 Free PMC article.
-
Three dimensional shape comparison of flexible proteins using the local-diameter descriptor.BMC Struct Biol. 2009 May 12;9:29. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-9-29. BMC Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 19435524 Free PMC article.
-
ViroBLAST: a stand-alone BLAST web server for flexible queries of multiple databases and user's datasets.Bioinformatics. 2007 Sep 1;23(17):2334-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm331. Epub 2007 Jun 22. Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17586542
-
Evolution of web services in bioinformatics.Brief Bioinform. 2005 Jun;6(2):178-88. doi: 10.1093/bib/6.2.178. Brief Bioinform. 2005. PMID: 15975226 Review.
-
Interactive text mining with Pipeline Pilot: a bibliographic web-based tool for PubMed.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2009 Jun;9(3):366-74. doi: 10.2174/1871526510909030366. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19519489 Review.
Cited by
-
A local average distance descriptor for flexible protein structure comparison.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Apr 2;15:95. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-95. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24694083 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Development of Shape Similarity Methods and Their Application in Drug Discovery.Front Chem. 2018 Jul 25;6:315. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00315. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2018. PMID: 30090808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ballester P, Richards W. Ultrafast shape recognition for similarity search in molecular databases. Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 2007;463(2081):1307–1321. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2007.1823. - DOI
-
- Funkhouser T, Min P, Kazhdan M, Chen J, Halderman A, Dobkin D, Jacobs D. A search engine for 3D models. ACM Transactions on Graphics. 2003;22:83–105. doi: 10.1145/588272.588279. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

